Category Archives: Uncategorized

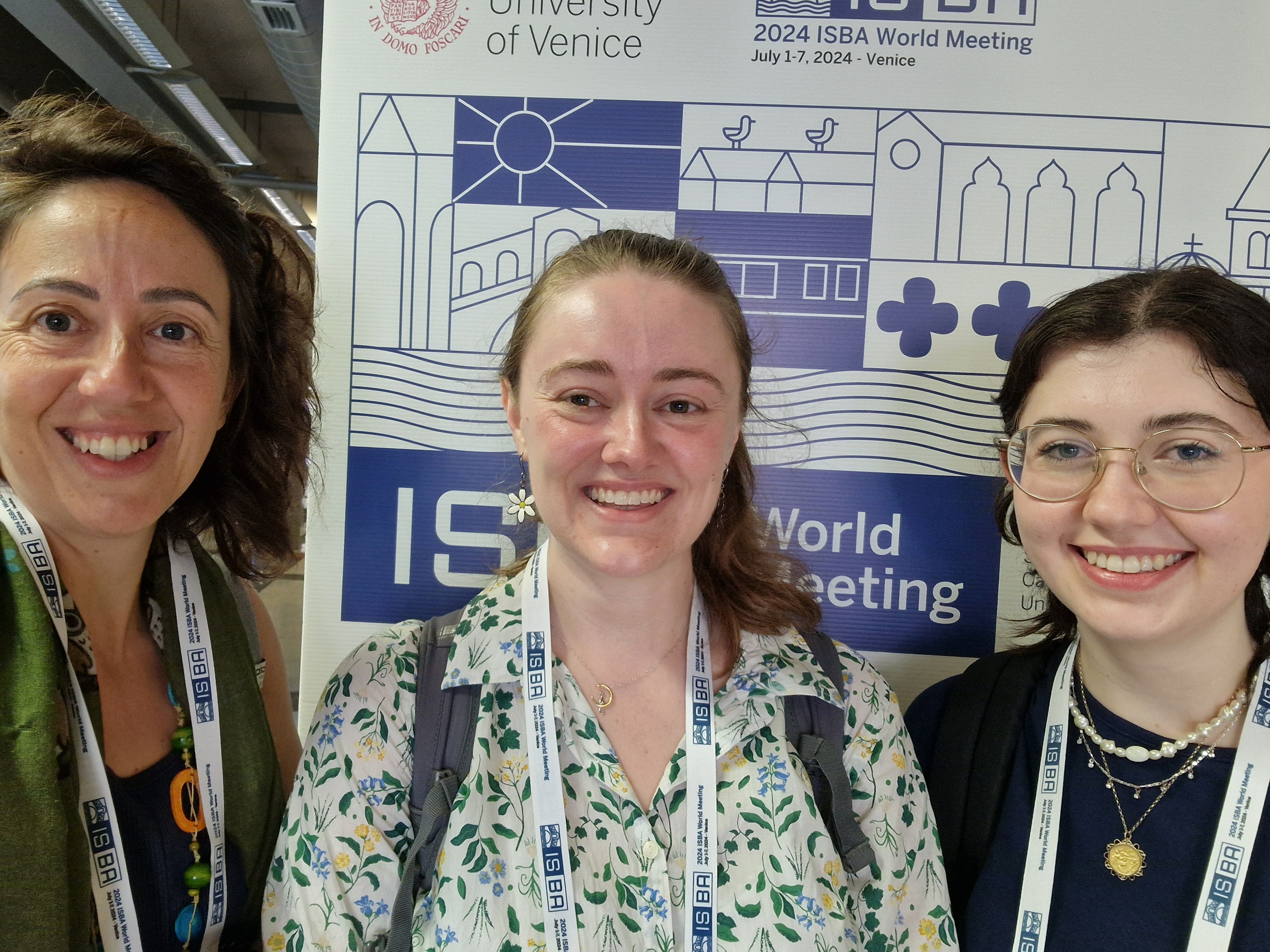
SE@K attending ISBA
Milly, Lucy and Eleni attended ISBA in Venice 1-8 July 2024 where they got to learn about the latest in Bayesian inference, as well as to listen to foundational talks on the topic by some of the most established researchers in the field.

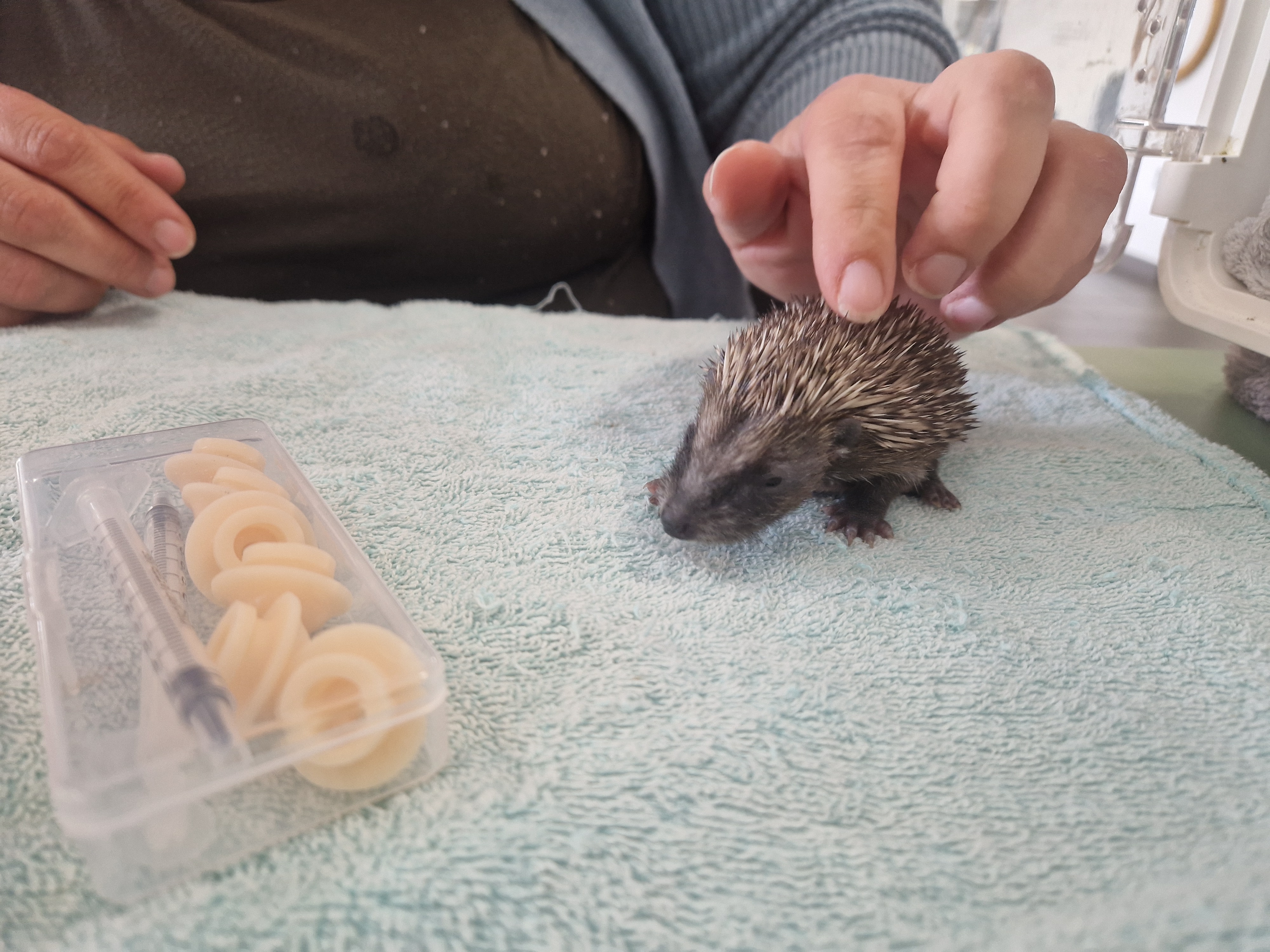
Stats gone wild
SE@K run the established and successful “Stats gone wild” event once more this year, with PhD students Milly, Tommy and Lucy running sessions on removal models, occupancy models and capture-recapture models, respectively.
The day also included a visit and information on hedgehogs by Lisa from Thorne Rescue and three two-week old hoglets!
New paper – Motivations and sensitivities surrounding the illegal trade of sea turtles in Costa Rica
Illegal wildlife trade can threaten biodiversity and economic development. Criminal enterprises may add wildlife products to their list of illicit goods by using established trade routes, networks, and individuals. On the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica, killing of sea turtles and removal of their eggs is commonplace. However, beyond conservation NGOs reporting evidence of illegal take, little is known about this activity. Through semi-structured interviews with law enforcement, community members, NGOs, and illegal harvesters, alongside anecdotal information and observations, we aimed to understand the motivations for illegal take. To cross-reference these findings, we assessed sensitivities surrounding illegal harvesting by asking the general public sensitive questions using the randomized response technique; a method used to elicit sensitive information whilst insuring the anonymity of respondents. We included a questionnaire to establish if differences in demographics affected the probability respondents would admit to a turtle-related crime. Our findings identified a rare example of illegal extraction of a wildlife product driven by motivations that were not exclusively livelihood based. We found the majority of illegal take was undertaken by relatively few individuals, dependent on narcotics. The most cited reason for illegal take was that turtle eggs could be used to procure drugs. Law enforcement was under resourced, and informants reported that prosecutions were rare. Local people preferred to purchase rather than harvest eggs suggesting the trade is supply-driven. Those interviewed did not generally regard the subject of illegal harvest as sensitive. Low education levels, high unemployment rates, and marginalization of certain groups may increase susceptibility to narcotics. Although substance misuse and addiction appear to drive illegal trade, associated poverty and marginalization may explain why drug dependency is so prevalent in Caribbean Costa Rica. Increased work opportunities and drug rehabilitation programs may assist in reducing illegal take of turtle eggs on nesting beaches.

SE@K at NSCE Summer Meeting
Several members of SE@K attended the NSCE summer meeting 26th-28th June in Swansea.
Diana Cole gave a presentation on “Bayesian Identifiability in Ecological Models”
Byron Morgan gave a talk entitled “Bucking the trend”
Fabian Ketwaroo talked about “Modelling roost count data”
Milly Jones talked about “Bayesian multi-species hierarchical distance sampling: Density estimation of
vertebrate species in Betampona Madagascar”. Her talk was runner-up in the student presentation competition.
Thomas Cheale’s talk was on “A General Framework for Balancing Privacy and Variance in Randomised
Response Methods”
Alex Diana talked about “Modelling DNA-based survey data”
Ioannis Rotous’ talk was on “Bayesian nonparametric models for batch-mark data”
They also enjoyed the sights in Swansea and the Welsh countryside


STEM for Britain 2023
Alex presented his work on modelling metabarcoding data at the 2023 STEM for Britain Competition
His poster described the novel modelling framework, introduced in the corresponding paper, and showed results from a data set on ingested DNA from a survey in China.

Spring term 2023 SE@K Thursday lunches
Spring term starts with the second half of Python training by Lena :-). Plan for the term in terms of sessions (and cake) below!
- 19th of January Session : Python training II – Lena; Cake : Lena & Daniel
- 26th of January Session : Daniel’s grant; Cake : Diana
- 2nd of February Session : HMM paper – Diana; Cake : Eleni
- 9th of February Session : HMM paper – Daniel; Cake : Oscar
- 16th of February Session : HMM paper – Takis (guest lecture); Cake : Alex
- 23rd of February Session : Variable selection/Hypothesis testing – Alex; Cake : James
- 2nd of March Session : HMM – Fred (guest lecture); Cake : Fabian
- 9th of March Session : Parameter redundancy – Daniel’s take; Cake : Tommy
- 16th of March Session Swedish register data – Bruno&Eleni ; Cake : Milly
- 23th of March Session : Swedish register data – Bruno&Eleni; Cake : Daniel
- 30th of March Session : Spatio-temporal models – Oscar; Cake : Diana
- 6th of April Session : eDNA data – Alex; Cake : Eleni

Se@k weekly lunches
The SE@K group are meeting weekly for research lunch and socialising 🙂
Autumn term
First week was about introductions and a tasty lunch at Dolce Vita!
Second week was about staff talking about their research interests, with Diana talking to the group about parameter redundancy.
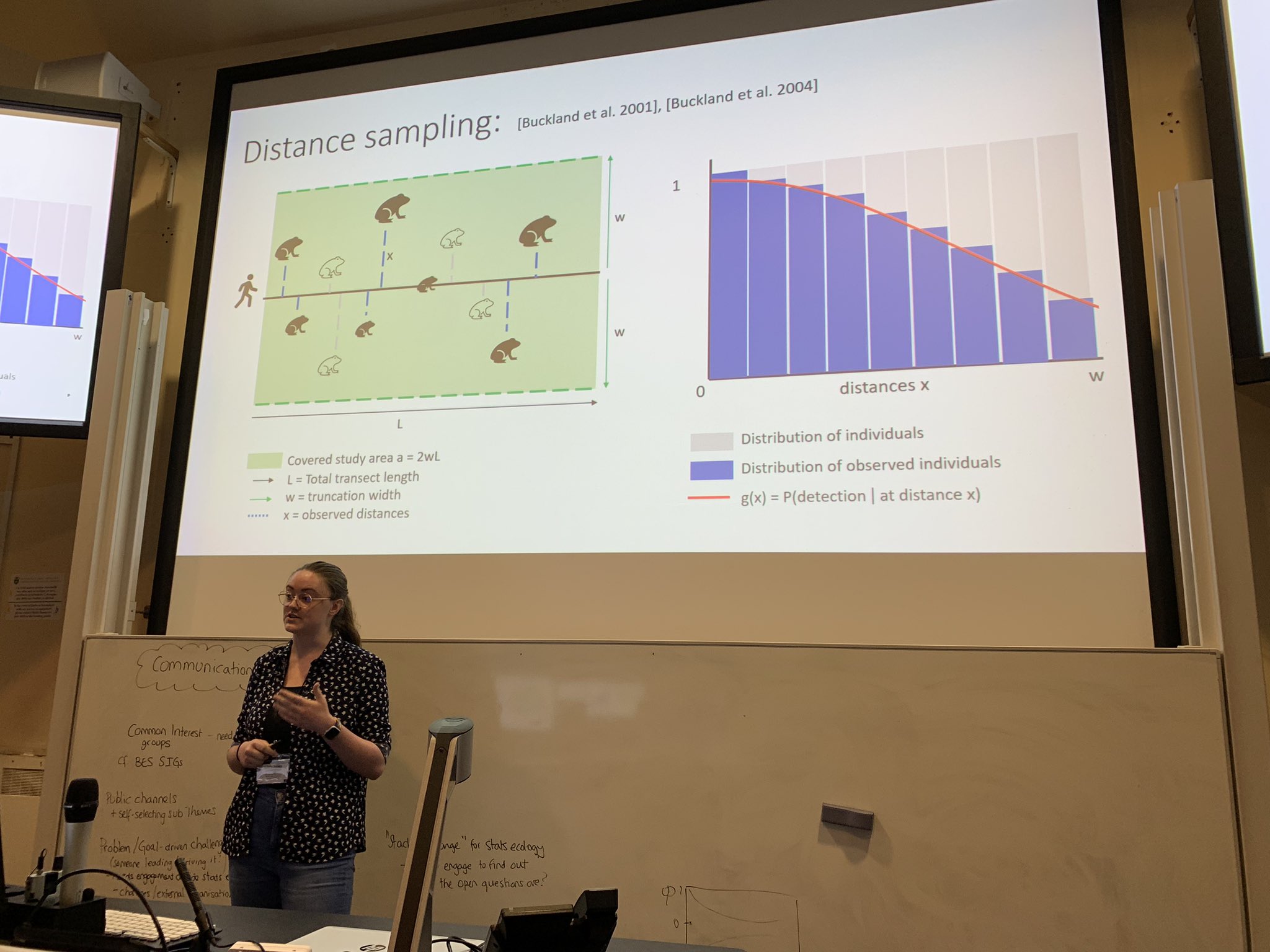
Third, fourth & fifth week were about research students talking about their research, with Tommy using randomised response techniques to estimate the proportion of people in the group who like/liked their supervisor (!), Milly talking about distance sampling, Ioannis talking about Bayesian non-parametrics and ABC and Lena talking about predator-prey models!
The term went on with learning about Gaussian processes from Alex, about PDEs from Eduard and about Python from Lena!
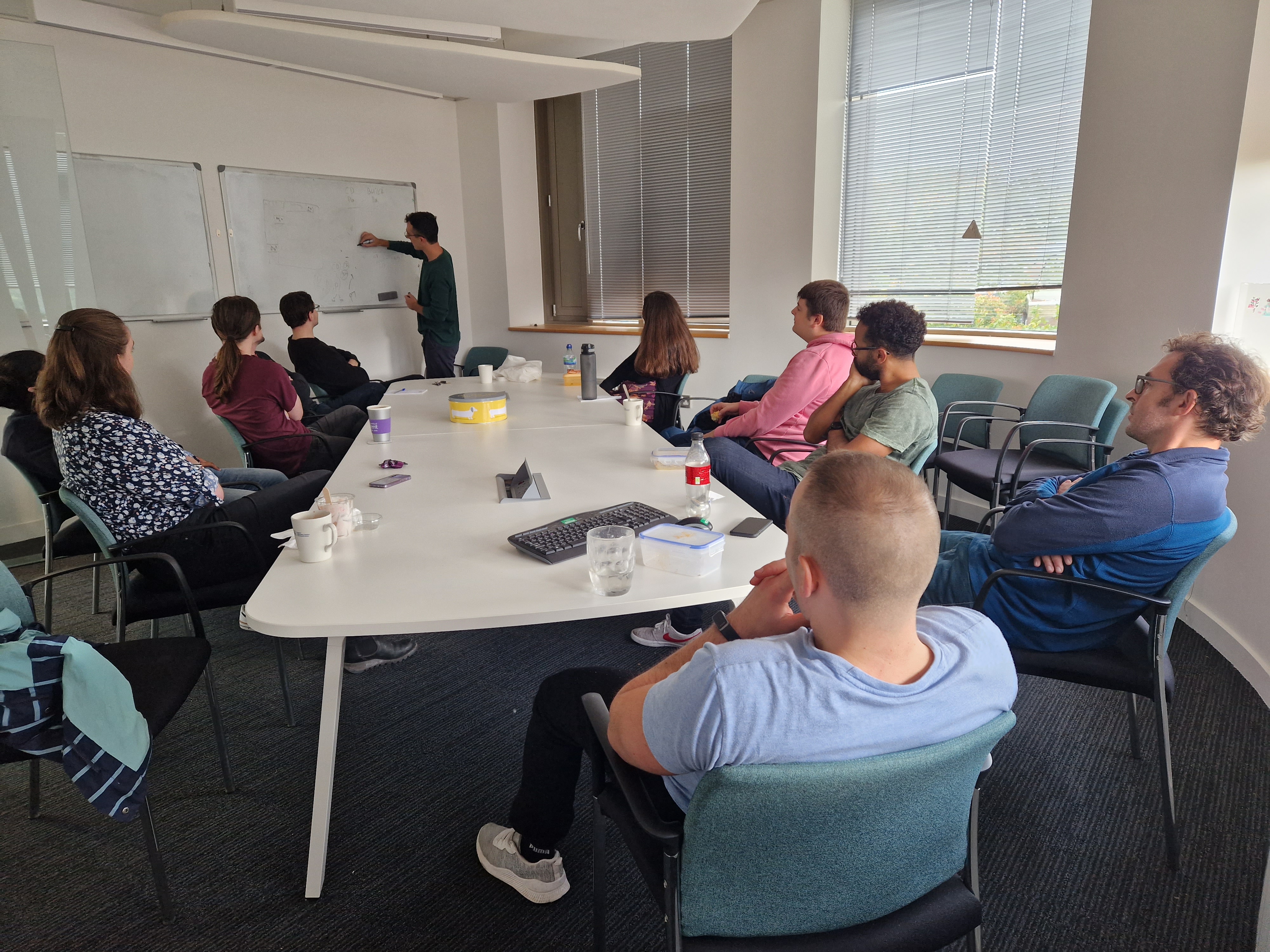
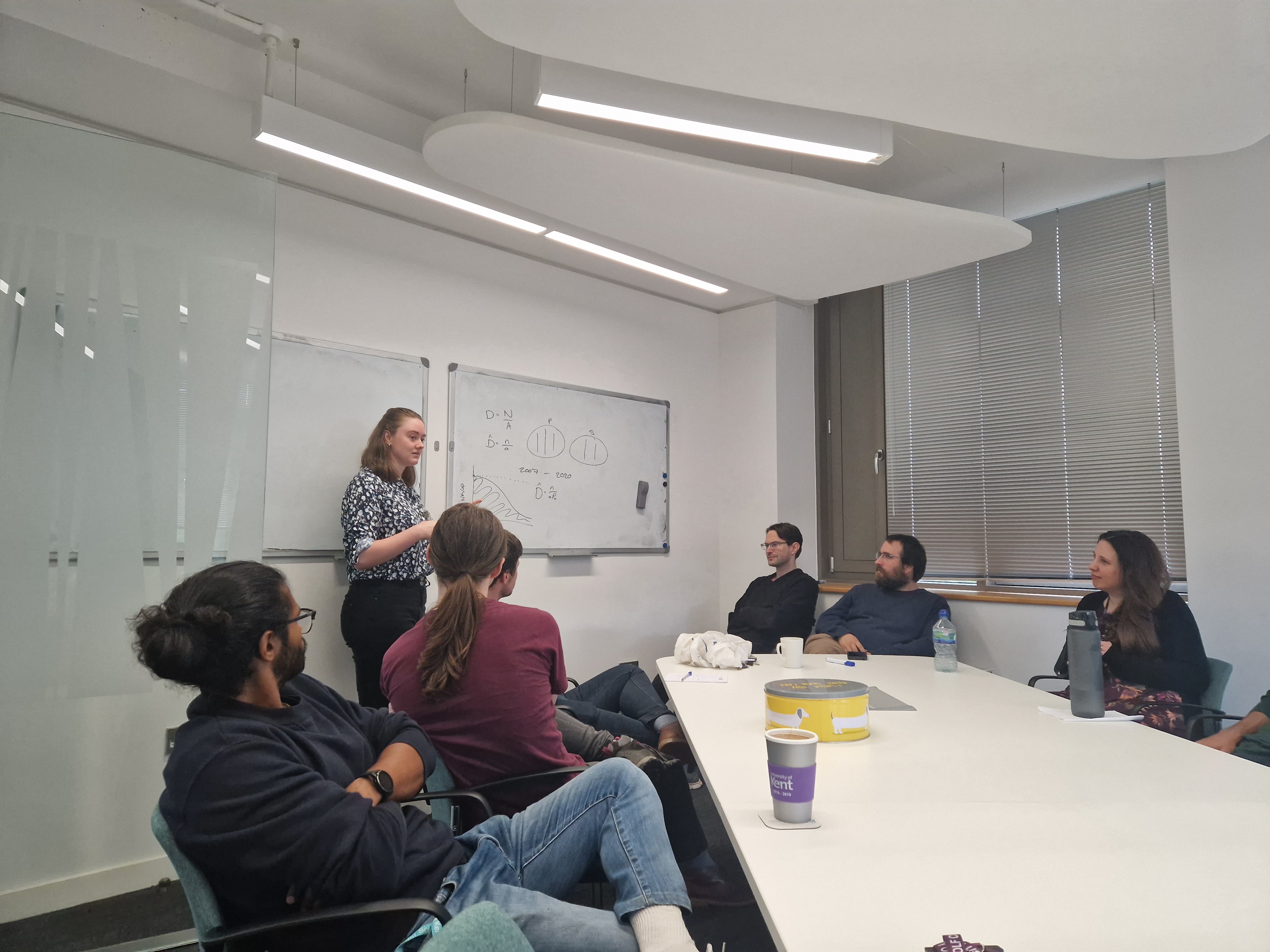
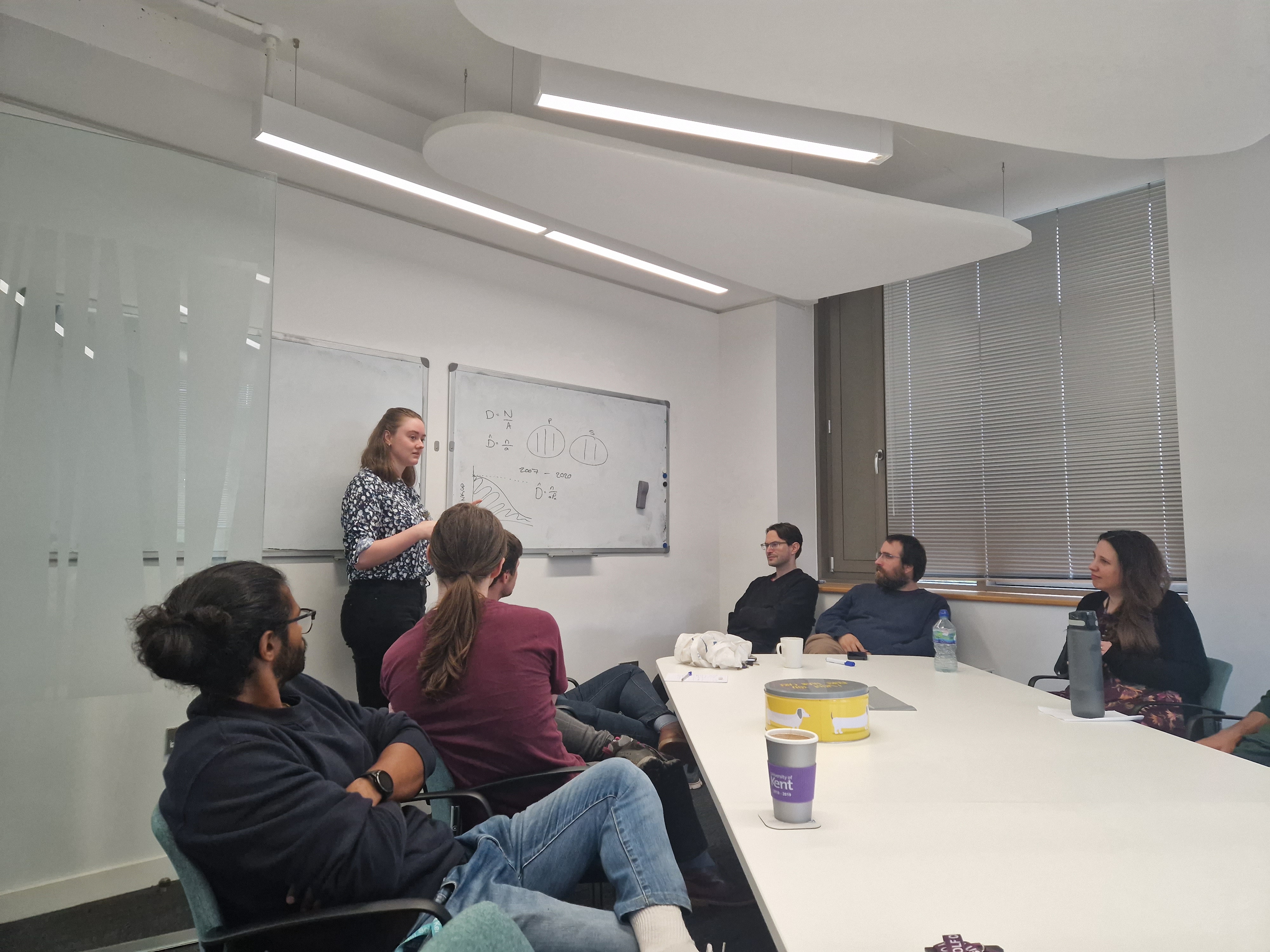






Welcome to new PhD student Milly Jones
Welcome to new PhD student Milly Jones who is supervised by Diana Cole and Eleni Matechou.
She is working with data collected by Madagascar Fauna and Flora Group (MFG), investigating the biodiversity in Madagascar. She will develop multi-species temporal models for the distance data collected.
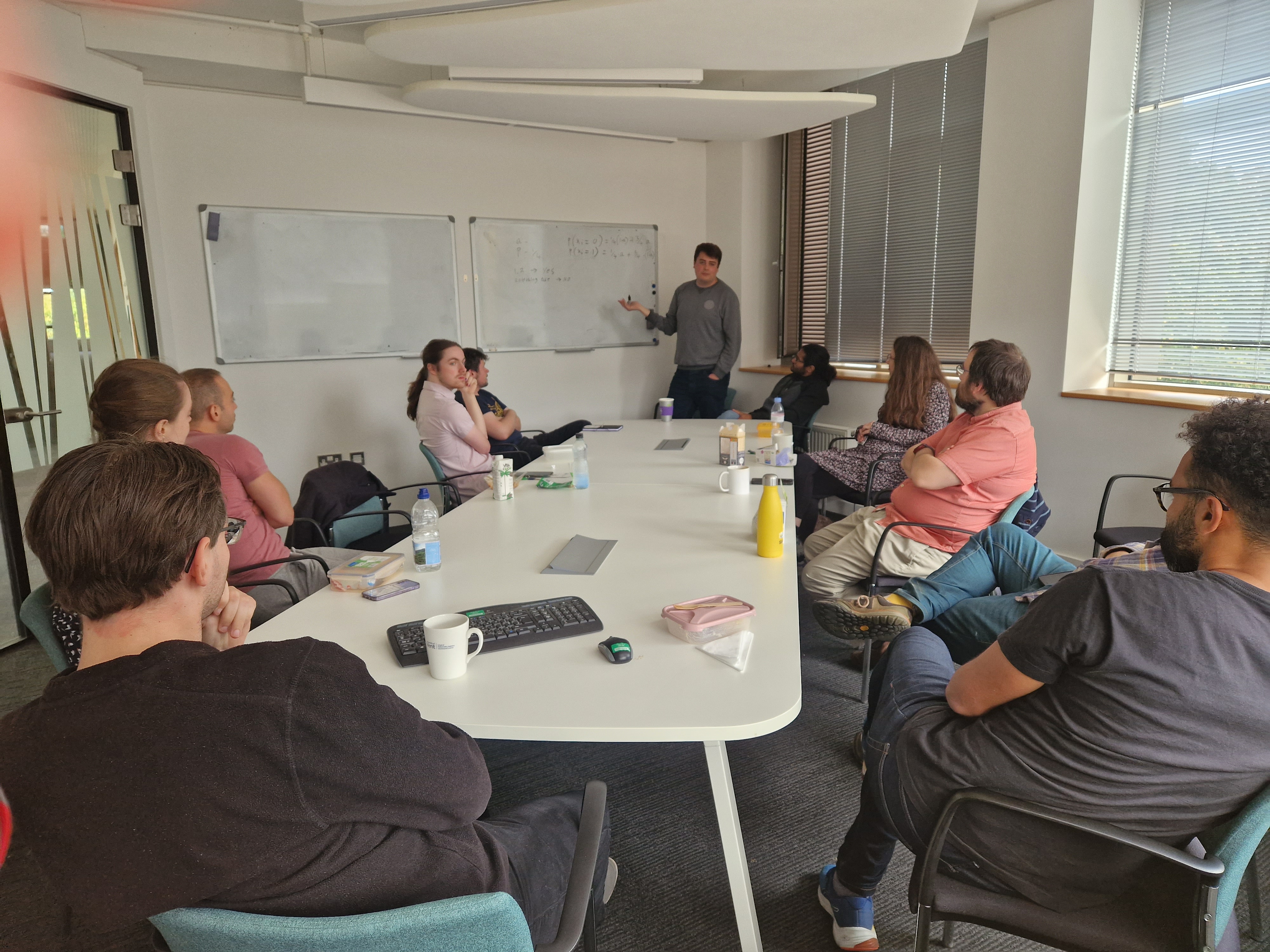
Picture shows Milly at the board explaining her PhD project to the SE@K group during our Thursday lunch time meetings.