11th February is International Day of Women and Girls in Science, which celebrates the vital role that women and girls play in science and technology. To mark this important day we are showcasing some of the material from the collection of Dame Stephanie Shirley CH.
Dame Stephanie “Steve” Shirley is an IT entrepreneur, successful businesswoman, and philanthropist. After arriving in the UK as an unaccompanied child refugee on the Kindertransport in 1939, Dame Stephanie developed a remarkable drive and energy that led her to follow a career in mathematics and computing at a time that was unusual for girls and women. She went on to lead a hugely successful software and programming company that focussed on providing employment opportunities for women, especially those with dependents.
Dame Stephanie then dedicated her time and resources to projects that she passionately believed in – advocating for women in the workplace and in technology, researching autism and supporting families of autistic children, and developing projects in computing and information technology.
In 2019 she donated the archive of her charitable foundation – The Shirley Foundation – to the University of Kent to establish the UK Philanthropy Archive.
Dame Stephanie is a STEM pioneer – and an inspirational figure to girls and women who are passionate about STEM subjects. This blog provides some information about Dame Stephanie, her early life and career and her many lifetime achievements, illustrated by items from the Shirley Foundation archive collection in the UK Philanthropy Archive.
Arrival in the UK
Dame Stephanie was born in Germany in 1933 as Vera Buchthal. At the beginning of the Second World War, her parents sent her and her sister to safety in Britain on the Kindertransport. They arrived in 1939 as unaccompanied child refugees and were placed in foster care in Sutton Coldfield. She adopted the surname of her foster parents and became Stephanie Brook.
Dame Stephanie received this commemorative cover (collectable envelope) after it was released in 1999 on the 60th Anniversary of the Kindertransport. It was designed by Stanley Kacher and has a special Liverpool Street postmark.
Career in mathematics and computing
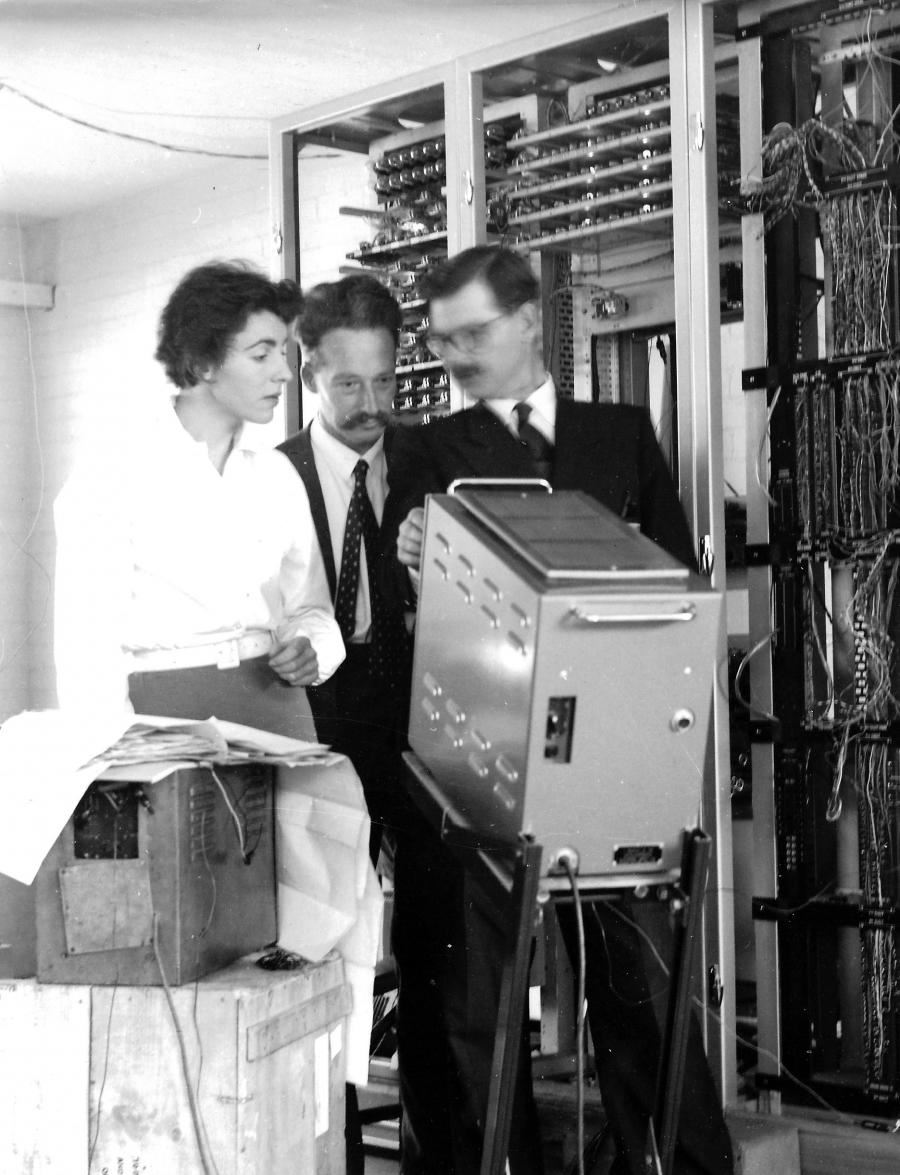
At school, Dame Stephanie began to show a talent for mathematics and took some extra lessons a local boy’s grammar school. She decided not to go to University, instead taking a role at the Post Office Research Station at Dollis Hill, north-west London, in 1957. She worked as part of the team that developed ERNIE (Electronic Random Number Indicator Equipment) an early computer which selected the Premium Bond numbers. She took extra evening classes to achieve an honours degree in mathematics. She then worked at CDL Ltd, the designers of the ICT-1301 computer.
This image shows one of Dame Stephanie’s copies of a research report on the work carried out by the team working on ERNIE (Electronic Random Number Indicator Equipment)– note her name Miss VS Brook, on the top right corner.
Freelance Programmers
After experiencing sexism, increasing discrimination against her gender, missed promotions and sometimes dealing with unwanted sexual advances, Dame Stephanie decided to run her own software company. With £6 initial investment, she founded her company Freelance Programmers, initially running from her dining room table. She employed a network of mainly female staff skilled at mathematics and programming. Freelance Programmers focussed on providing flexible working opportunities for women, especially those with dependents. This was especially important for Dame Stephanie and her husband Derek Shirley, after their son Giles was born in 1963.
While fairly successful, the company was still experiencing difficulty in attracting work. Dame Stephanie changed her name to “Steve” Shirley, used this name on her business correspondence, and achieved a vast improvement in success. Dame Stephanie became known as ‘Steve’ from this point onwards.
Freelance Programmers was later known as FI, then Xansa, and was later acquired by Steria now part of the Sopra Steria Group. In 25 years as the Chief Executive, Dame Stephanie developed the company into a leading business technology group which pioneered new work practices and changed the position of professional women along the way.
The Shirley Foundation archive also contains annual reports and papers from the development of Freelance Programmers and its transition to FI Group Plc – including these distinctive annual reports from FI Group.
Philanthropy
Dame Stephanie’s philanthropy focussed on her professional and personal interests: IT due to her skills and career in software and computing, and autism research due to her personal experiences after her son Giles was diagnosed with autism in 1966.
She decided early on in her philanthropic career that she wanted to support funding and research during her lifetime, and structured the Shirley Foundation with the aim to spend all of its funds, which was achieved in 2018 having made more than £67million in grants.
This included funding residential care homes and developing schools that more specifically met the needs of children and adults with autism. This focus continued after Giles sadly died in 1998. Dame Stephanie also focussed on funding research into autism, and improvements in practice relating to autism, to benefit autistic people and their communities.
Dame Stephanie also supported many IT and computing projects, and work that supported the role and development of women in STEM subjects.
An avid art collector, Dame Stephanie donated her entire collection of contemporary art and sculpture to the charity Paintings in Hospitals and to Prior’s Court School.
Lectures, Awards and Achievements
Dame Stephanie has delivered thousands of talks and lectures over 50 years about her work in computing and mathematics, the development of her business, her focus on flexible roles for women and motivation for and focus of her philanthropy. One example is this speech on Women in Data Processing – delivered in June 1980 while she was Vice-President of the British Computer Society.
Over her lifetime, she has achieved many awards and public recognitions of her achievements as a leader in the IT sector.
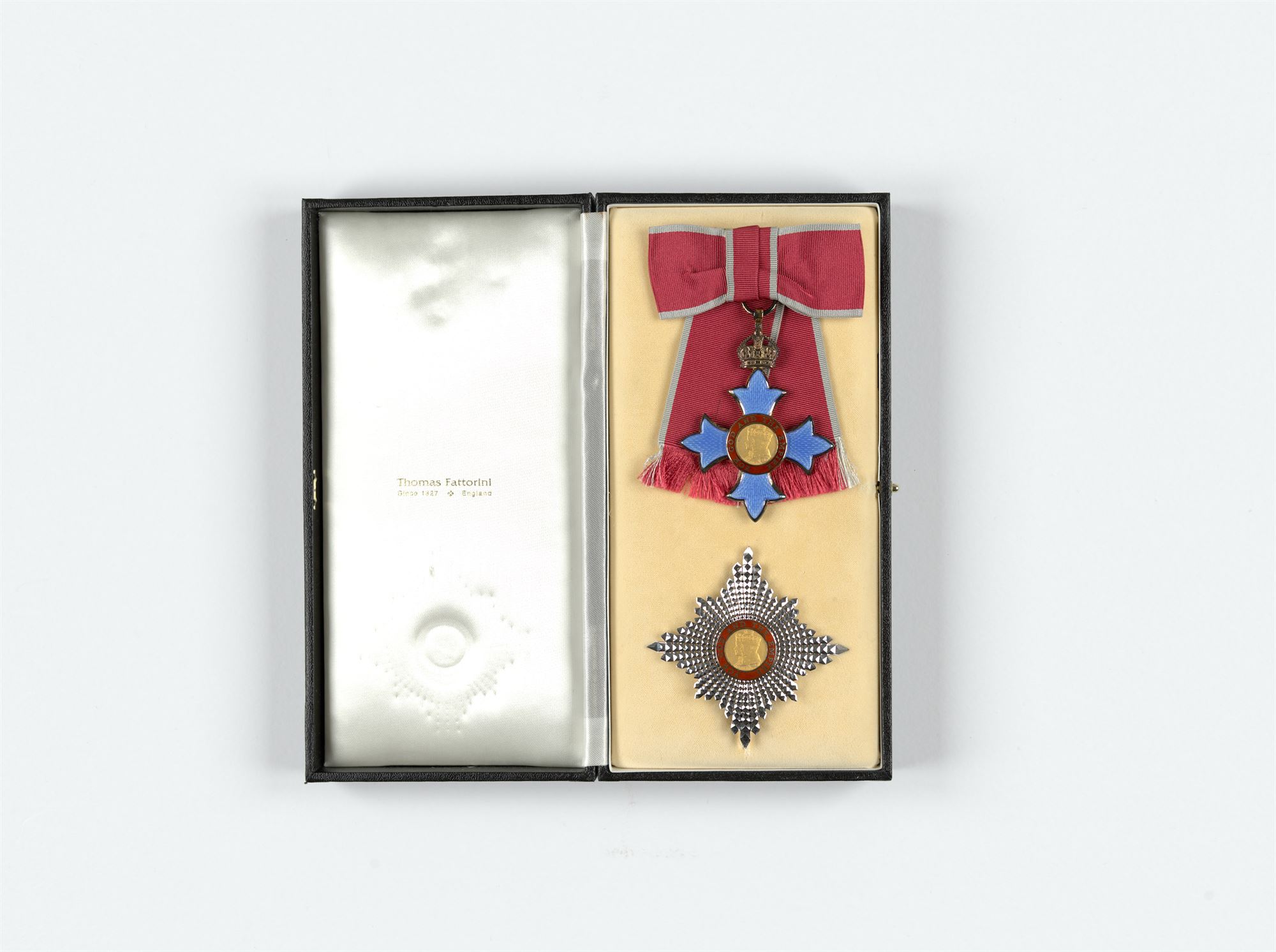
In 1980 she received an OBE – for her services to Industry. In 1992 she was elected as the first women Master of the IT livery company, the Worshipful Company of Information Technologists, and was also the first women President of the chartered Computer Society. She was appointed a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering in 2001. In the millennium honours Dame Stephanie was awarded with a DBE for services to IT, and then in the Queen’s Birthday Honours in June 2017 she was awarded the prestigious Order of Companions of Honour (CH) for services to IT and to philanthropy.



















 Perhaps one of our most enigmatic items, this Greek vase has been part of Special Collections for a long time, and represents those stand alone items which are not part of any collection, but are unique, rare or valuable within their own right. Although the provenance of the vase is unknown, information with the item does suggest that this is an ancient treasure.
Perhaps one of our most enigmatic items, this Greek vase has been part of Special Collections for a long time, and represents those stand alone items which are not part of any collection, but are unique, rare or valuable within their own right. Although the provenance of the vase is unknown, information with the item does suggest that this is an ancient treasure.
 This lovely image is of Hewlett Johnson, Dean of Canterbury Cathedral from 1931-1963. A contraversial figure in his lifetime, owing to his stalwart support of Communist regimes including Stalin’s Russia and Mao’s China, Johnson travelled widely.
This lovely image is of Hewlett Johnson, Dean of Canterbury Cathedral from 1931-1963. A contraversial figure in his lifetime, owing to his stalwart support of Communist regimes including Stalin’s Russia and Mao’s China, Johnson travelled widely.  The Muggeridge Collections include a variety of photographs of mills and other rural subjects, which date from 1904 onwards. William Burrell Muggeridge and his son Donald were fascinated by the vanishing rural life in Britain and across the wider world. Donald’s role in the Second World War gave him the unlikely opportunity of photographing mills across Europe, and he later supplemented this collection on family holidays. The set of images of mills in Portugal were taken in April 1966: this photograph is of a group of tower mills at Abelheira near Esposende. As well as documenting lost architecture and ways of life, the Muggeridge father and son were also innovative in their use of developing photographic technology.
The Muggeridge Collections include a variety of photographs of mills and other rural subjects, which date from 1904 onwards. William Burrell Muggeridge and his son Donald were fascinated by the vanishing rural life in Britain and across the wider world. Donald’s role in the Second World War gave him the unlikely opportunity of photographing mills across Europe, and he later supplemented this collection on family holidays. The set of images of mills in Portugal were taken in April 1966: this photograph is of a group of tower mills at Abelheira near Esposende. As well as documenting lost architecture and ways of life, the Muggeridge father and son were also innovative in their use of developing photographic technology. Since the autumn of 2014, the University of Kent has hosted the nascent British Stand Up Comedy Archive, which was founded with the deposit of materials from comedians Linda Smith and Mark Thomas. This archive includes a wealth of audio visual materials and is growing rapidly. Alongside the collections of another four comedians, materials include records of venues, interviews with comedians and some magazines relating to the early Stand Up Comedy scene.
Since the autumn of 2014, the University of Kent has hosted the nascent British Stand Up Comedy Archive, which was founded with the deposit of materials from comedians Linda Smith and Mark Thomas. This archive includes a wealth of audio visual materials and is growing rapidly. Alongside the collections of another four comedians, materials include records of venues, interviews with comedians and some magazines relating to the early Stand Up Comedy scene.
 Information about the Melville family.
Information about the Melville family. Alongside our archival collections, Special Collections also holds a number of rare books. Written by Thomas Heywood, this 1690 edition of
Alongside our archival collections, Special Collections also holds a number of rare books. Written by Thomas Heywood, this 1690 edition of