Join us for a series of workshops and talks in May and June 2023 that explore how we tell stories of migration and movement. Our series of events includes creative and art workshops, talks providing insights into refugee stories and practical consideration of how to ensure refugee stories are preserved and remembered.
This series follows our June 2022 exhibition – Reflections on the Great British Fish and Chips – where a volunteer research group selected items for display from Special Collections and Archives that explored themes of migration, movement and global food production. This display of original items accompanied an exhibition created by reportage artist Olivier Kugler, and writer Andrew Humphreys, which revealed everyday stories of migration through illustrating the lives and experiences of fish and chip shop owners across Kent.
Bookings for each event can be made by emailing specialcollections@kent.ac.uk
We look forward to welcoming you at one or more of this events series – to share stories and experiences and build understanding and compassion in relation to migration and movement of people across the world.
Wednesday 24th May 2023: 12.30pm
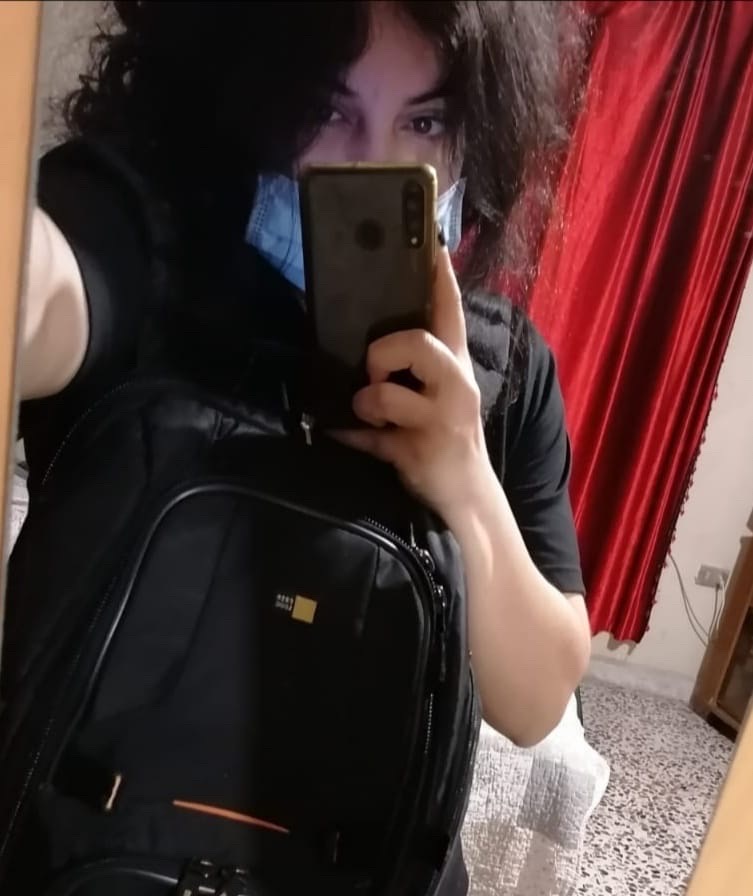
Photography in protracted displacement as a tool of activism: Basma El Doukhi in conversation with Rania Saadallah (Stateless refugee and photographer)
An exciting launch event for the Telling our Tales series of activities, following our Reflections on the Great British Fish and Chips exhibition events in 2022.
Join us for a discussion about Rania’s work in the Reflections on the Great British Fish and Chips exhibition and her work in the Palestinian camps of Lebanon. This will include her personal journey as a third-generation stateless Palestinian refugee who is using photography as a tool to share and tell tales about Palestinian refugees, mainly women, in the camps of Lebanon. Rania will describe how this tool helped her to challenge the status quo and narratives about refugees within the camps and outside them.
The conversation will be followed by a Q&A and a session for reflection on the way forward.
This is a hybrid event which can you join in person or remotely. The event is open and free for all to attend. Rania will be speaking to us from Lebanon. The talk will be shown on a screen in the Templeman Library – room D G 02 – near the Nexus area.
Please email specialcollections@kent.ac.uk to book/register your place, or request to join the talk remotely.
About Rania:
Rania Saadallah is a third-generation stateless Palestinian refugee who uses photography as a tool to share and tell tales about Palestinian refugees, mainly women, in the camps of Lebanon. Rania says: “Five years ago, I started her story in the world of photography. When it was enough to make me know people more, their pain and joy, in addition to creating a kind of love for people’s faces more. Despite this time, until this moment, every photography experience creates a state of fear and anxiety, as if it was the first time I was photographing. I moved between filming workshops, stories from the camps, exhibitions, and many stories that took a part of my soul.”
About Basma:
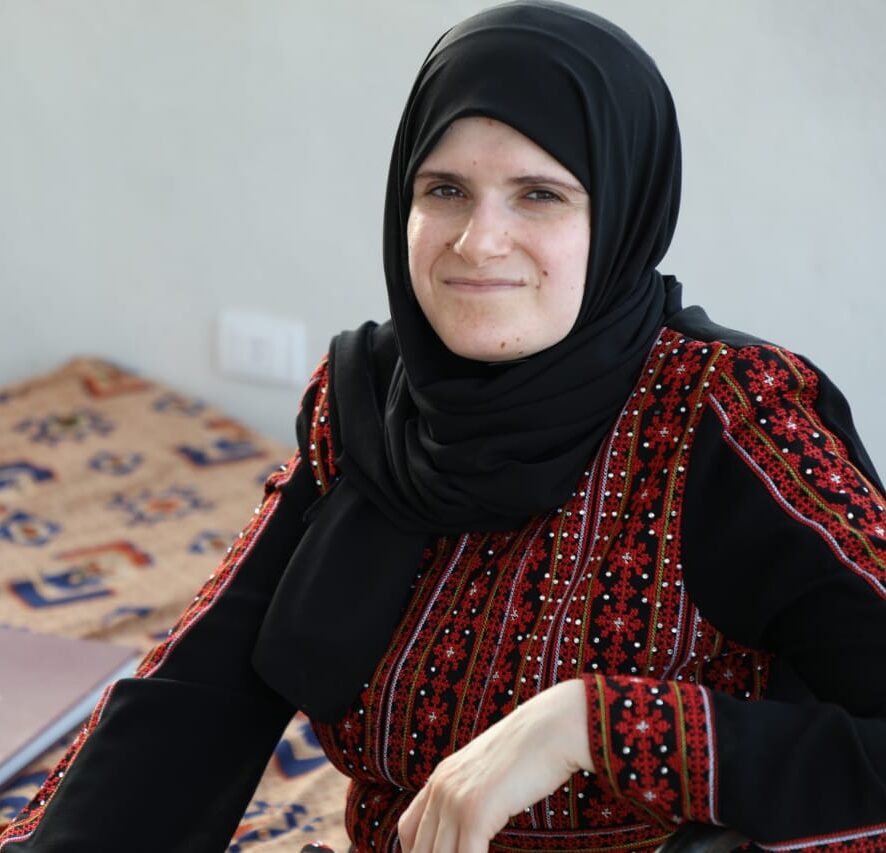
Basma El Douhki is a PhD Researcher in Migration Studies with the Global Challenges Doctoral Centre (GCDC) at the University of Kent. For many years Basma has been active in humanitarian and development work with refugees and asylum seekers within UNHCR, UNRWA and international NGOs in Lebanon and Syria. Basma’s own lived experience as a refugee, and her post-graduate studies in Emergency and Development Studies, have influenced her work exploring the nature of refugee-led organisations and the factors conditioning their impact and interventions.
Wednesday 24th May 2023: 2.30pm
Visual Story-telling with Adïam Yemane
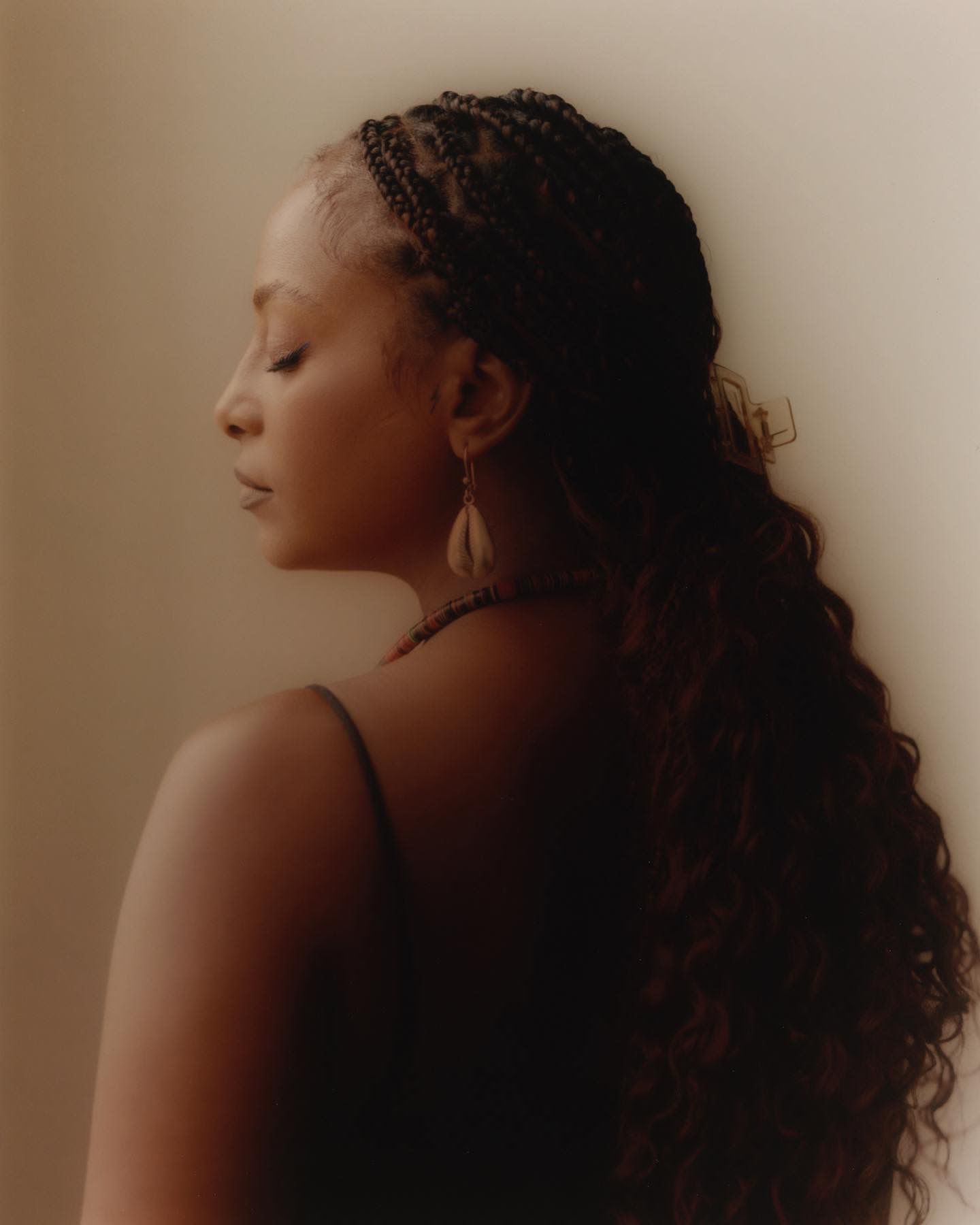
This workshop is led by Adïam Yemane, an Ethiopian Eritrean visual artist and travelling storyteller, with a focus on social justice and community development.
Adïam will lead a workshop taking participants on a short journey on how stories are told visually and how we can naturally weave these disciplines into our daily lives. During the workshop, Adïam will present her work and the work of other Visual Artists, encouraging wider group discussions and more intimate smaller group discussions.
Each participant is invited to bring a photograph for a group exercise. This could be a personal story or something you have seen before that tells the story of migration, which you like and are happy to share with the group.
About Adïam:
Adïam works as a freelance Portrait and research photographer focusing on social justice and community development. Longing for consistent change and and movement inspires her to travel and document the world. World peace and sustainability are Adïam’s main focus. Through art, Adïam expresses heartfelt stories from around the world that facilitate the viewer with a greater understanding.
The workshop will take place in the Templeman Library – Room D G 02 – near the Nexus area.
Please email specialcollections@kent.ac.uk to book/register your place.
Wednesday 7th June 2023: 1.30pm
Creative Expressions of Migration and Movement with Maryam Sandjari Hashemi

Maryam Sandjari Hashemi, Multidisciplinary Artist and Spiritual Coach. (Image copyright: Danial Emani)
London based Iranian artist, Maryam Sandjari Hashemi, will deliver this creative workshop, sharing her artwork and her journey as a migrant artist with participants. Maryam’s work brings past and present together reflecting her personal journey from Iran to the UK and aspects of both cultures.
Participants are invited to bring an object and share its story with the group, and will be actively creating artwork using drawing, collage and other techniques. No previous experience of creating art is required for this workshop, just some along and have fun.
About Maryam:
Maryam Sandjari Hashemi is a Multidisciplinary Artist and a Spiritual Coach. Her art practice includes Visual Art, Performance and Textile rooted in her upbringing in Iran and inspired by her colourful everyday life. Her paintings have been telling the story of her life journey and she has been exploring different themes such as identity and inner ecology. Most of her works are dense with information and imagery that communicates with viewers subconscious mind often acting like portals that could take viewers on a deep psychedelic journey.
Maryam has run many community art workshops for diverse groups especially migrants and refugees focussing on creating a playful atmosphere where participants could feel safe to express themselves and empowered to explore different artistic techniques. Her workshops are accessible and suitable for all artistic abilities and she especially encourages participants with little or no experience in creating art.
The workshop will take place in the Templeman Library – Room D G 02 – near the Nexus area.
Please email specialcollections@kent.ac.uk to book/register your place.
Wednesday 14th June 2023: 1pm
Archiving Stories of Migration: Paul Dudman and Beth Astridge
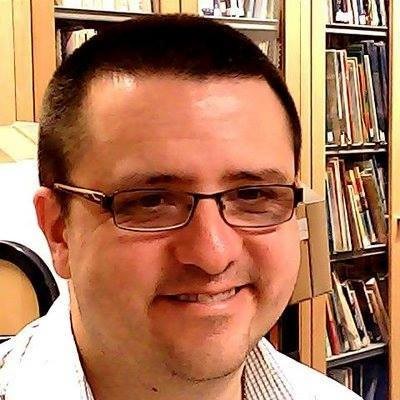
This thought-provoking workshop will be delivered by Paul Dudman, Archivist at the University of East London where he is responsible for the Refugee Council Archive, and Beth Astridge, University Archivist at the University of Kent. The workshop will explore examples of how stories of migration and movement can be reflected in archive collections and some of the challenges in capturing the life experiences of refugees in the archive record.
Paul and Beth will provide a range of examples from archive collections for participants to view and encourage group discussion about the stories that these different archives tell. Groups will then be encouraged to consider the challenges and ethics of recording stories and experiences of migration and movement using scenarios and examples in the collections at the University of East London.
The workshop will take place in the Templeman Library – Room A 1 08 – next to the Special Collections and Archives Reading Room and offices. Please email specialcollections@kent.ac.uk to book/register your place.
About Paul:
Paul Dudman is the Archivist at the University of East London Archives whose collections include the Refugee Council Archive. Paul’s research interests are focussed on refugee history and the role of archives in documenting and preserving the personal narratives and life histories of migration.
Paul is the Editor for the journal Displaced Voices: A Journal of Archives, Migration and Cultural Heritage, hosted on the Living Refugee Archive online portal, and is a co-convenor of the IASFM (International Association for the Study of Forced Migration) Working Group for the Archiving and Documentation of the History of Forced Migration.
About Beth:
Beth Astridge is the University Archivist in Special Collections and Archives at the University of Kent. In May/June 2022 Beth collaborated with Basma El Doukhi to deliver a co-curated exhibition – Reflections on the Great British Fish and Chips, where volunteers explored the University Special Collections and Archives for items relating to the theme of migration, movement and global food production.
Wednesday 21st June 2023: 2.00pm
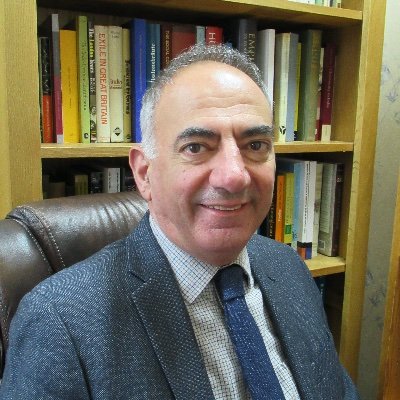
Migrants, Fish and Chips, and Britishness: a talk by Professor Panikos Panayi, Professor of European History, De Montfort University
Professor Panikos Panayi will deliver this mouth-watering talk on the history of Britain’s most popular take-away meals, and explore the role of migrant communities in the development of the fish and chip trade.
Panikos was featured in the exhibition ‘The Great British Fish and Chips’ originally displayed at the Turner Contemporary, Margate and Canterbury Cathedral in June 2021. In June 2022, the University of Kent Special Collections and Archives hosted a new viewing of the exhibition. This was exhibited alongside a co-curated display of original archives from the University’s collections, selected by a volunteer group of researchers, with a focus on migration, movement and global food production. Professor Panayi’s talk will provide an opportunity to see the original exhibition panels once again.
The talk will take place in the Templeman Library – Room D G 02 – near the Nexus area. Please email specialcollections@kent.ac.uk to book/register your place.
About Panikos:
Professor Panikos Panayi is Professor of European History at De Montfort University. He has published widely and his research interests include the history of immigration and interethnic relations, the history of food, the First World War, German history, the history of London, and the history of the Cypriot people.
Professor Panayi’s research into the history of Fish and Chips was published in 2014 as ‘Fish and Chips: A History’. In the book he unwraps the origins of fish and potato eating in Britain, and describes the meal’s creation during the 19th century. He also explores the connection with issues of class and identity and the extensive ethnic affiliations of the dish. Fried fish was widely consumed by immigrant Jews before spreading to the English working classes in the early nineteenth century, and by the 20th century other migrant communities such as Italians played a leading role in the fish-and-chip trade.