SC&A are delighted to present the first of a series of blog posts by one of our volunteers, Dr. Daniella Gonzalez.
Having finished my doctoral studies and eager to get back into the archives to kick-start my career in the archival sector, I began to volunteer at Special Collections & Archives (hereafter SC&A) at the University of Kent in February 2020. There is nothing I like more than uncovering the mysteries that lie in the records before me. It is these materials that tie us back to the past and to the people who lived it. We get an insight into their experiences, thoughts and those they interacted with, as well as the processes that governed their everyday lives. In this piece I want to tell you a bit about what I’ve been doing and what I’ve learnt.
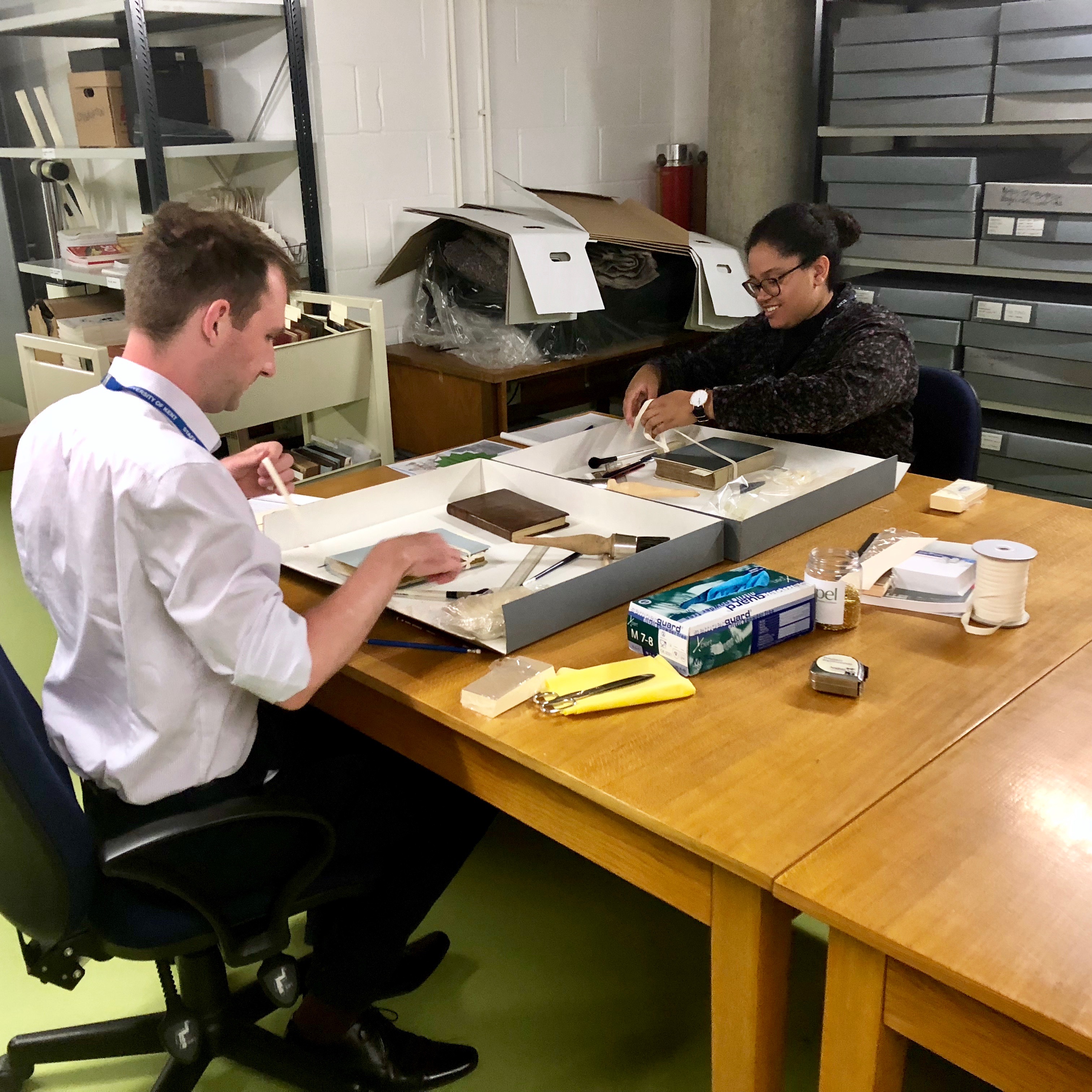
As a volunteer at SC&A, I had the fantastic opportunity to work with the early modern indentures that form part of the Ronald Baldwin collection, a selection of pre-1900 material that focuses on the county of Kent and which was collected by Baldwin, a local historian. The items in this part of the collection span the fifteenth to eighteenth centuries, informing us about the lives of those that lived in the county of Kent under the Plantagenet kings of England up to the first Georgian monarch. My task was to sort and list the documents into a spreadsheet so it could be uploaded into the online catalogue; to transcribe and translate the documents; and to repackage them into archival quality enclosures to ensure their long-term preservation.
As soon as I laid eyes on the documents I would be working on I knew that this was the perfect project for me. Opening the box was the familiar sight of vellum, parchment and paper, as well as the script that is typical of early modern legal documents – to my delight there was even a late medieval document dating to 1 July 1425!
Those utilising these records will also notice that some are written in Latin and others in English. Some, like in the document below, produced on 10 February 1645, whilst Charles I was still king, are even written in both (as you can see the document is divided into two section, the Latin section, which is a preamble of sorts is at the top, and below the document continues in English), so be ready to put your Latin skills to the test!
Several of these items are in relatively good condition seals that have been slightly damaged and some slight staining of particular records.
As part of my introduction to the project, the University Archivist explained to me how archive catalogues are structured as a hierarchy, with different levels representing different aspects of the collection. Whilst I’ve had my fair share of visits to archives, I’d never realised that there is a catalogue hierarchy of sorts.
Knowing this was key in order for me to carry out my work on the early modern legal records I had before me. Thanks to the introduction, I knew that when cataloguing material, archivists need to capture several key bits of information, such as the level of these records – in this case ‘item’ – the repository they are held in, the collection they belong to and their reference number, which uniquely identifies these records as particular items. Other essential information to include are the date they were produced, the language they were written in, the condition of the record, what type of record it is and a description of the records that describes its content.
Whilst sorting them into chronological order and cataloguing these records has been the central part of this project, I have also been able to put my palaeography skills to the test. Palaeography is the study of old handwriting and, whilst a medievalist by trade and having studied palaeography previously, some of the early modern handwriting was a little tricky at times. Totally worth it though when you encounter such beautiful illustrated initials like that on the right, dating to the reign of Charles I!
I have also been putting my palaeography skills to good use and producing transcriptions for researchers and the general public alike, which will be made available soon!
I’ll be producing some posts about my archive experiences with SC&A, so watch this space for more on early modern indentures and the daily lives of Kent’s early modern communities!
The catalogue entries for this collection are now live and can be viewed here: https://archive.kent.ac.uk/TreeBrowse.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&field=RefNo&key=RB%2fDOC%2fIND

















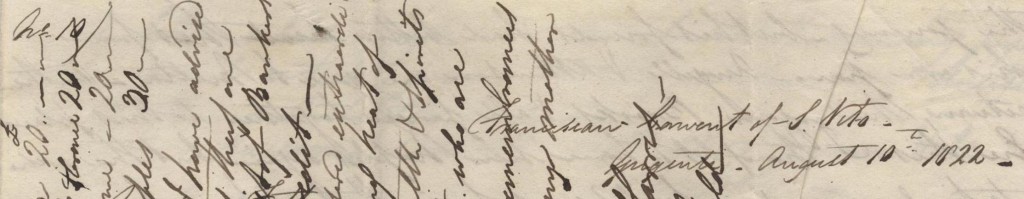



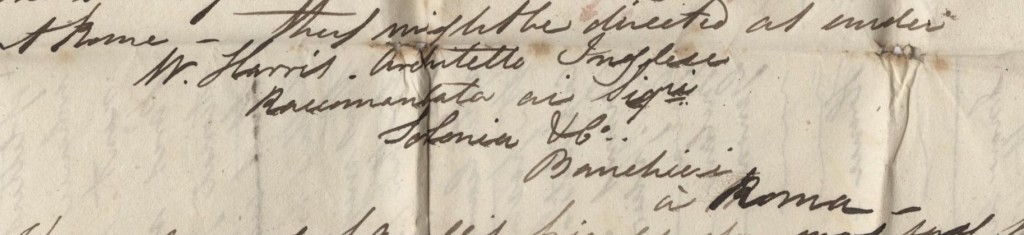
 enthusiasm for discovering more about his journey has diminished; in fact, the other day I was idly glancing through a holiday brochure and saw a package tour around Sicily, covering Mount Etna, Palermo, Siracusa and Taormina and got a bit over excited. No, this isn’t my planned holiday for this year (not at that price!) but this does follow the journey which William and his friends took nearly 200 years ago. In fact, it looks like William was part of the team which undertook some of the earliest work on these now very popular tourist destinations.
enthusiasm for discovering more about his journey has diminished; in fact, the other day I was idly glancing through a holiday brochure and saw a package tour around Sicily, covering Mount Etna, Palermo, Siracusa and Taormina and got a bit over excited. No, this isn’t my planned holiday for this year (not at that price!) but this does follow the journey which William and his friends took nearly 200 years ago. In fact, it looks like William was part of the team which undertook some of the earliest work on these now very popular tourist destinations.




