Karen Brayshaw, Special Collections and Archives Manager
As 2024 draws to a close it is my great pleasure to look back on another busy and exciting year of activity in the University’s Special Collections and Archives. The only change to our Team this year is that we said goodbye our project archivist Daniella in the summer. Daniella worked with us on two funded projects, the David Drummond Pantomime Collection and the collection from the Craigmyle Fundraising Consultants. The project included sorting, listing, repackaging, and making the two collections accessible and discoverable. You may have seen what she got up to on our social media channels. We wish Daniella well in her new venture.

Daniella with some Aladdin material from the David Drummond Pantomime Collection.
The whole team have been amazing colleagues throughout the year – especially when I had to step back from work for a few months in order to recover from a health issue – I am very lucky to work with such an awesome team! Although I’ve missed seeing the work that has taken place in the last three months, I have been able to follow the exciting events through colleagues and social media. One of the many highlights of the year for me was the amazing exhibition celebrating Kent’s rich mining history. It was a great example of collaborative working with our volunteers and in this case we owe many thanks to Amy. It proved to be a popular attraction, and we had many visitors to the gallery, including external groups. As well as overseeing and co-curating our wonderful exhibitions, Beth has been busy working with the philanthropic community to grow the UK Philanthropy Archive and raising the funds to enable us to catalogue them. I’m looking forward to 2025 when much of this work will take place and the records will be added to our catalogue. Beth also has a loyal group of volunteers who come in regularly to work on the University archive, which will be super helpful next year as we approach the University’s 60th anniversary. Beth has also worked to deliver new and innovative sessions for external groups, and it was a joy to see the pantomime collection being utilised to stimulate the students from Canterbury College exploring ideas for their projects.
Clair has had an amazing year, working to get more of our collections listed, repackaged, and added to the online catalogue for all to see. A significant amount of this has been made possible through the excellent work Clair does with student work placements and volunteers. I was especially pleased to see the Holt’s Bairnsfather collection being listed and repackaged – you can read more about it below. Clair has also been busy this year overseeing loans of collection items for external exhibitions, which is another way of sharing our amazing collections with wider audiences.
Christine has also been busy devising new sessions and introducing new material to the seminar groups, exposing the academics and students to the richness of our collections. In 2023 we were pleased to receive the Louis James collection and Christine has done an amazing job of cataloguing the whole lot! The collection is already proving its value in enriching our teaching offer and Christine is being a brilliant advocate for it. It’s also very satisfying to witness the great work Christine and her volunteers are doing with our theatre programme collection.

Items from the Louis James Collection
Alex is keeping the Phase One rig busy and producing amazing images from the cartoon and theatre collections. This enables greater access as well as supporting the preservation of the collections. Mandy continues to beaver away making sure our cuttings collection is kept up to date. At the same time, she has been digitising some original art works and sheet music. Sam has been working on digitising and cataloguing collections in the British Cartoon Archive, specifically Lawrie Siggs and Donald Rooum Collections. You can now find the records for Lawrie Siggs on our catalogue. Jacqueline completed cataloguing the Arnold Rood collection, Jack Reading and Colin Rayner’s collection, Charles Lewen’s collection, and books from the David Drummond Pantomime collection. It’s always a joy to see what treasures she brings back from the basement!
Our colleagues from the Curation and Discovery team, Stu, Matthias and Emma have been working with us one day per week and continue to make big strides in dealing with our British Cartoon Library backlog as well as our digital cartoon collection and various book collections, making them available to everyone.
I never cease to be amazed and humbled by the talented people that come to support us in our work. Our volunteer projects this year have yet again been hugely successful – many thanks to everyone who has helped us in 2024! – and we look forward to working with our current and new teams of volunteers in 2025.
If you are on campus do drop by the Templeman Gallery, Block A|1. The team are currently installing a wonderful exhibition about pantomime (Oh yes they are!) which I promise will not disappoint you. The new listening station has some lovely content on it. And do keep an eye on our social media channels for updates on our associated events.

Sneak preview of our upcoming pantomime exhibition ‘Magnificent! Spectacular!’
Clair (Digital Archivist)
Once again, the year has gone by super-fast and I feel as if I can only just recall all the amazing things the team has achieved this year, but there are a few stand outs for me.
Firstly, we are so lucky to have worked with some amazing volunteers and placement students this year.I supervised a group of three students – Lizzie, Harvey and Nirvanna – who worked on packaging and preserving some ceramic objects in the British Cartoon Archive. You can read a blog post about this work here. I’ve also had the pleasure of working with our lovely volunteers, one of whom, Grahame, not only donated a collection of theatre programmes to us last February but also committed to listing them all for us! He’s now finished that work but continues to volunteer with us, working now on our Max Tyler collection.

Completed packaging of Holt Bairnsfather Collection objects.
We’ve received some fabulous material for the British Stand-Up Comedy Archive this year which I’ve had the pleasure of sorting, accessioning and cataloguing, including three fan collections (Laura Grimshaw’s Teenage Obsessions, Richard Gill’s ‘A Rich Comic Life’ Collection, and the Joseph Champniss Collection), the Lakin McCarthy Entertainment Ltd Collection, and a collection of material from Stewart Lee.
Our loan service has been busy again this year, with British Cartoon Archive material going out to the Herne Bay Cartoon Festival and Imperial War Museum, and a continuing loan of a Nick Garland cartoon to the V&A that is part of an international touring exhibition.

Image of the V&A exhibition ’Alice: Curiouser and Curiouser’ installed at the V&A Musuem in South Kensington.

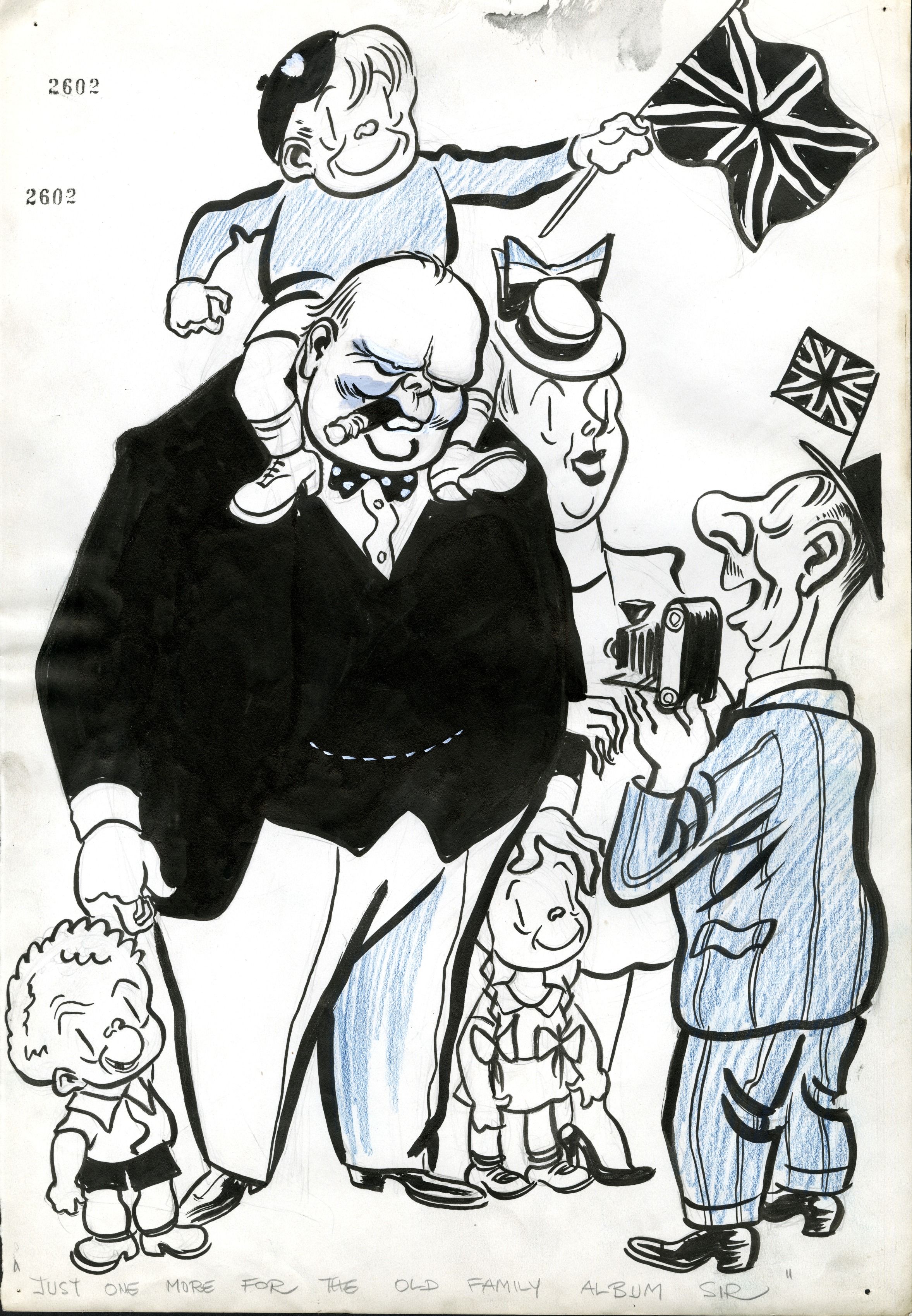
The poster for the ‘Churchill in Cartoons’ exhibtion outside the doors of the IWM.
It’s such a pleasure that we’re able to share our collections to the wider public in this way and I really enjoy being able to make connections with institutions in Britain and abroad through supporting their exhibitions.The exhibition at the IWM (Churchill in Cartoons: Satirising a Statesman) opens from 29 November 2024 to 23 February 2025, so do check this out if you can. We were very lucky to be invited to the Private View of the exhibition, which we very much enjoyed. It’s a fabulous look at Churchill’s political career through satirical cartoons. And I’m delighted to say we already have two exciting loan requests in process for next year, so things aren’t slowing down!
Lastly, I was thrilled to organise a Halloween event with my colleagues Beth and Christine this year. Called ‘Ghost Stories’, it was a behind-the-scenes tour of our archival stores with a difference! Attendees were titillated with (battery-powered) candle-lit readings of classic ghost stories. The event was very well received, and we hope to do another event next Halloween, albeit with a new spooOoOOooky theme.

An image of a spectre in our stores, lit only by emergency lights and (battery) tea lights
Beth Astridge (University Archivist)
Exhibitions in the Templeman Gallery
We run a regular programme of exhibitions in the Templeman Gallery and our ‘Mining in Kent’ exhibition was a particular highlight! Using a range of our archive material this exhibition told the story of the history of mining in Kent, from the early days of discovering the Kent coalfield to the impact of the 1984 Miners’ Strike. We were able to showcase material from several collections including the Richard Richardson Mining Collection, the British Cartoon Archive, the British Stand-Up Comedy Archive, and the Labour and Socialist Newspapers. We held several tours of the exhibition as well as a launch event and have been really pleased with the local interest and feedback about exhibition and our events. We are particularly grateful to one of our volunteers, Amy Green, who assisted with research, writing panels and captions, and installing the exhibition.
We also curated a virtual version of this exhibition which you can view on our exhibitions page.

Image of Coal Not Dole leaflet from the Richard Richardson Mining Collection
Another exhibitions highlight this year has been our collaboration with the Brook Rural Museum on an oral history project relating to memories of hopping and hop production in the Brook and Wye area of Kent. This resulted in an exhibition in our Gallery space featuring recordings of the oral history interviews alongside material that described the history and future of hop production in Kent. This exhibition will be on show again in 2025 at the Brook Rural Museum, so make sure you plan a visit!

Page on Picking Hops from Ann and Jane Taylor, Rural Scenes or a peep into the country: For children (1840), a book in our Children’s Literature collection (S 519.T23 TAY CLC
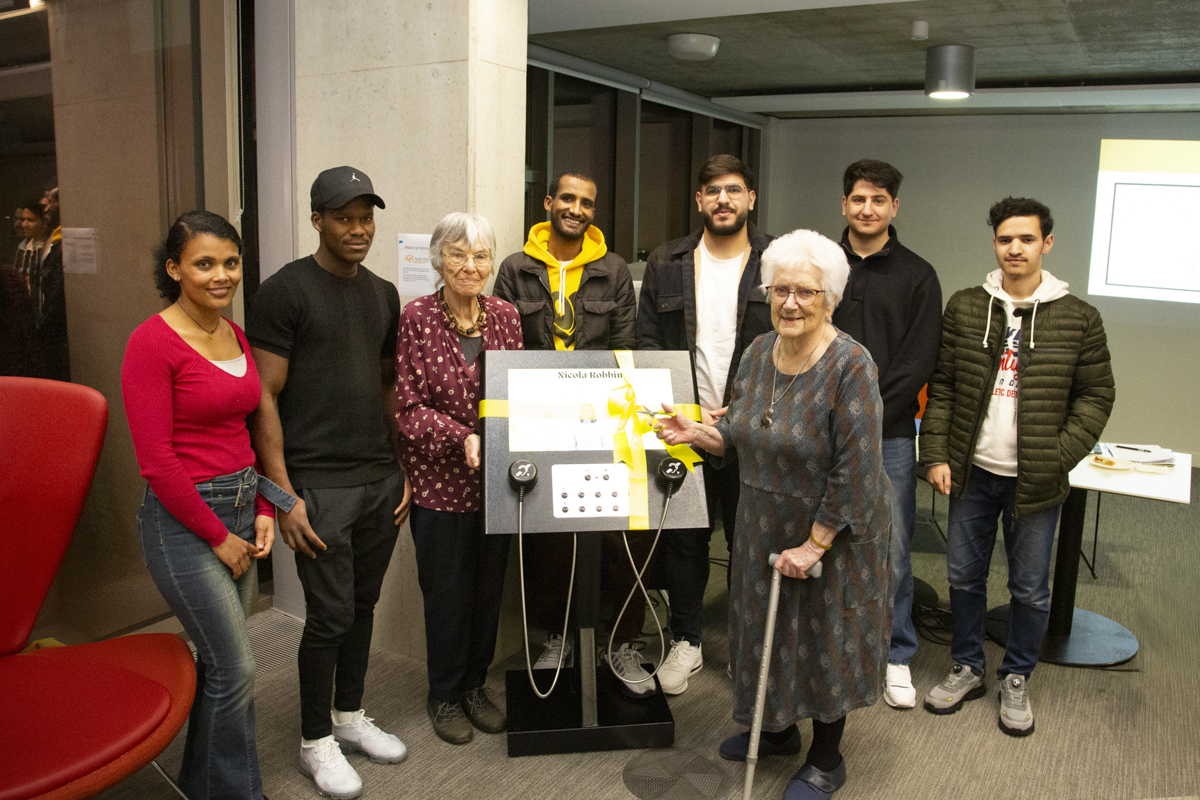
Listening Station

Our Listening Station in action during the exhibition, Local Stories: Memories of Hopping around Brook and Wye, Kent
The oral history exhibition gave us the opportunity to show off our new listening station in the Templeman Gallery. This is a new audio-visual unit that allows us to upload video and audio material for viewers to listen to/watch in the exhibition space. It is hearing aid enabled and has two listening speakers – so please watch out for future opportunities to discover more of our video and audio collections – including material for our next exhibition on the David Drummond Pantomime Collection.
Philanthropy and Fundraising

Page from early records of the National Benevolent Fund showing some of the early donors/subscribers, National Benevolent Fund Archive
The UK Philanthropy Archive continues to thrive and a highlight this year was receiving some important new collections. In July we received the collection of the National Benevolent Fund – a charity established in 1812 which used a subscription model to support ‘distressed gentlewomen’ with pensions and annuities and later supported those experiencing poverty. The collection had been identified as a collection at risk by The National Archives and we were pleased to play a part in saving this fascinating collection and giving it a home.
In September we were delighted to receive the archive collection of the John Ellerman Foundation along with a grant to enable the repackaging and cataloguing of this important collection of a foundation established by Sir John Ellerman, once Britain’s richest man, and the family behind the Ellerman Lines and Wilson Lines shipping business. Look out for more about this in 2025 when we start the cataloguing process.
And finally, also in September, we received the Jack Petchey Foundation archive. Sir Jack Petchey was a businessman and philanthropist who started a taxi business, a second-hand car business and later a property business, generating the wealth that he dedicated to charitable work and philanthropy focussed on young people through his Foundation. The full catalogue for this collection will appear on our website soon.
This year we have also made great strides towards cataloguing the Craigmyle Fundraising Consultants collection – a project that will be completed in 2025! The partial catalogue is available now to view on our website.
University Archive
In the University Archive we are gearing up to the University’s 60th anniversary celebrations later in 2025. One aspect of this will focus on music and live music performances on campus, and I have enjoying communicating with alumni who have memories and sometimes photo evidence of fantastic bands and gigs they attended. Volunteers Peter Stanfield and more recently David Blair have been doing an amazing job researching and logging the gigs and bands who played at the University since we opened in 1965. We are looking forward to making this complete list available for researchers and former students highlighting what it was like to work, study and enjoy live music on campus throughout its history!
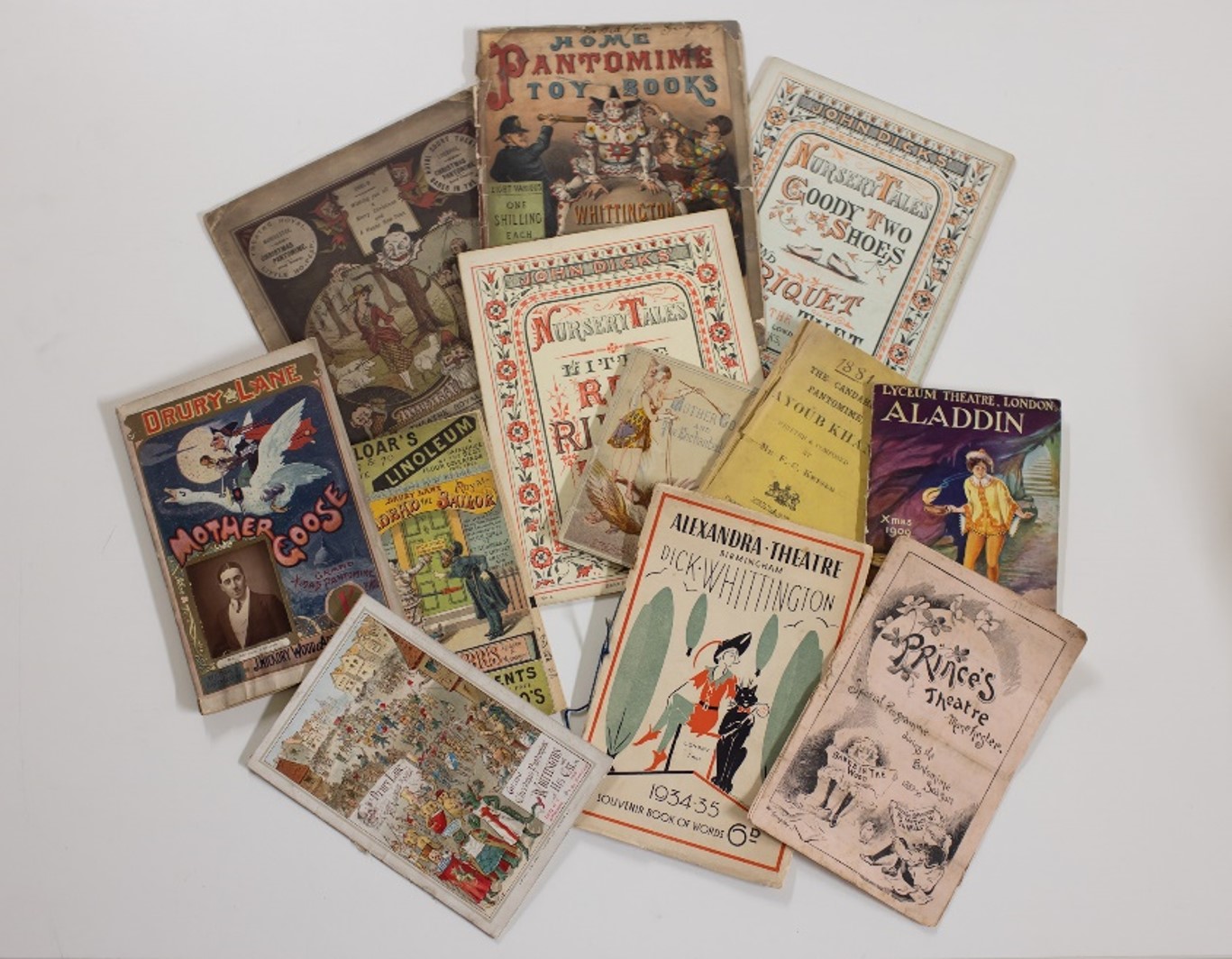
Cataloguing the David Drummond Pantomime Collection
The Archives Revealed funded cataloguing project was almost(!) finished this year by our brilliant Project Archivist Daniella Gonzalez.

Students from EKC Canterbury College studying the David Drummond Pantomime Collection – image courtesy of Amanda Sefton-Hogg, Canterbury Festival.
We are using Daniella’s work to inform the final exhibition of the year – Magnificent! Spectacular! – which will showcase this fantastic collection and tell the story of the history of pantomime from the early days of the Commedia dell’Arte to the modern extravaganza we know today!
A panto project highlight was working in collaboration with the Canterbury Festival and EKC Canterbury College to bring more than 100 students onto campus to use the David Drummond Pantomime Collection as inspiration for coursework across subjects such as fine art, textiles, graphics, and photography. You will be able to see a couple of the students creations in our exhibition, and we were super pleased that this highlight was featured in The National Archives publication, A Year in Archives.
Christine Davies (Special Collections and Archives Coordinator)
I had the great pleasure this year of cataloguing the collection of literature gifted to us by a former professor of Victorian and modern literature at Kent, Louis James. The Louis James Collection primarily comprises literature of the Caribbean and African diasporas, but there are also important theoretical and historical works on race, colonialism and slavery too. Many of us have heard of Olaudah Equiano, the famous abolitionist, but Mary Prince is less well known – born into slavery in Bermuda, her dictated memoirs were published in London in 1831 and reprinted twice in the same year. Further highlights in the collection, for me, include an unpublished typescript of Derek Walcott’s play Franklin; diverse artisanal, cloth-bound books published by the Writers Workshop (a small printing press established in Calcutta); the plethora of Caribbean poetry which details the migrant experience in Britain with irony, sometimes anger, always charisma, and which – on the page and in performance – was completely innovative. Kamau Brathwaite created the ‘Sycorax video style’ by combining customized typefaces with irregular page layouts; others’ are marked by their rhythmic similarity to reggae (dub) and/or their fusion of dialects. Amongst the African literature, there are works that reflect on Apartheid, delve into Anasi lore, and diverse anthologies that celebrate the continent’s diversity (from works of magical realism to social justice, from Nobel prize winners to Onitsha market literature); one of the most powerful works, for me, is Ngũgĩ wa Thiong’o’s Devil on the cross, the manuscript of which was written in secret, from gaol, on toilet paper. The collection amounts to more than 1000 items and is fully accessible on Library Search.

Examples of Writers Workshop publications in the Louis James Collection, as displayed for our South Asian History Month Archives tour
I’ve also had good fun this year devising new material and seminars for Kent’s School of English, which gives students the opportunity to handle rare books and consider the intricate cultural and socio-political contexts of their period of study. The explosion of print in the eighteenth century gave rise to numerous newspapers and periodicals, the latter typically published monthly. These new arenas of print were not only used to disseminate information but also direct public taste and opinion and even shape literary developments. Fiction could be serialised in these monthly publications and biographies and gossip columns fuelled an emerging celebrity culture, giving voice to more obscure figures since forgotten – how many of you have heard of the blind poet and early disability advocate, Thomas Blacklock (1721-1791)? Did you know that The Lady’s Magazine (1770-1847) provided inspiration for both Jane Austen and the Brontë sisters?

Volunteer Amelia Bocskei working on photographs found in Terry O’Brien’s programme collection
As Beth and Clair have both mentioned, we couldn’t do all we do without the invaluable support of our volunteers, and this year has marked a significant leap forward in the management of our theatre programme collections.
Through the collected efforts of Ladaya Berrier, Amelia Bocskei, Stefana Ivanova, Rhea Nurice Lempert and Jessica Mulroy, thousands of programmes have been organised, re-packaged, and listed on spreadsheets, and this will be used to create and enrich catalogue records next year. This work has already enabled us to consolidate our existing holdings of theatre programmes and refine our collecting priorities; it has also enhanced our engagement work by filling gaps in performance history. Our volunteers have also found the experience greatly beneficial, stating how much a privilege it has been “to preserve a voice from the past” and “interact with original historical documents.”
Alex Triggs (Digitisation Administrator)
The high-resolution digitisation of the British Cartoon Archive collections continued throughout 2024 utilising the Phase One photographic rig. This year the focus has been on the original cartoon artwork of Mac (Stanley McMurtry), cartoonist with the Daily Mail. Mac’s career with the Daily Mail began in 1971 and lasted for almost five decades. As a result, this collection contains circa 5000 items of which approximately 80% have been digitised during the year. In addition, a selection of playbills from the David Drummond Pantomime Collection have also been digitised over the past 12 months. Many of these date back to the 1850s and require careful handling as they are extremely delicate.

Left: Our ‘digital kitchen’; Right: a playbill from the David Drummond Pantomime Collection.
On the audio-visual side, I have continued the digitisation the University of Kent Archive collection of vulnerable analogue magnetic audio cassette tape recordings. Moving forward, I am now beginning to address the significant number of at-risk VHS video cassette recordings contained within a several of the Special Collections, perhaps most significantly the British Stand-Up Comedy Archive.
Mandy (Special Collections & Archives Assistant)
I always enjoy scanning our Carl Giles collection every year for the Giles Annual, they are always fun. I have scanned 6,000 cartoons in our Hector Breeze collection, which is so interesting to do. I’m now working on another cartoon collection – the Alan Ralph Collection – which is now being digitised. The song sheets in the Max Tyler Music Hall Collection have also been so lovely to scan as some of them are so vintage and very delicate. Overall, it has been a busy and interesting time for 2024!

Hector Breeze cartoon (HB0012)
Jacqueline Spencer (Project Curation and Discovery Administrator)
I began the year cataloguing Arnold Rood’s collection of books on theatre. He collected widely around a strong nucleus of works by and about the extraordinary theatre designer (and son of Ellen Terry) Edward Gordon Craig. Next, I catalogued the extensive set of 20th century theatre periodicals in the Reading Rayner collection, then I added books from David Drummond Pantomime Collection to the library catalogue supporting the project to catalogue his archive. He collected books related to pantomime including both scholarly works on the origins of the genre such as ‘The reminiscences of Thomas Dibdin at the Theatres Royal, Drury Lane ..’ of 1824, and some lovely, illustrated children’s books such as ‘Naughty Cinderella’ from 1936. Charles Lewsen’s books on theatre arts enhance our collection scope in this area, his collection contains more 19th century material. This delicate personification of ‘La Comedie’ with mask and barely visible sprites over her shoulders is the frontispiece from his copy of ‘Masques et bouffons (Comedie Italienne) with text and drawings by Maurice Sand, Paris 1862.

‘La Comedie’, Masques et bouffons (Comedie Italienne) with text and drawings by Maurice Sand, Paris 1862
The Holt Bairnsfather books came next, with a bottom-up view from the trenches of the 1914-18 World War. As this year ends, I have started cataloguing the Muggeridge Book Collection. Focusing on windmills in the U.K. and the Netherlands, William Burrell Muggeridge and Donald Muggeridge were also interested in industrial archaeology and country life and work and sought out locally published pamphlets which can be hard to find as well as substantial scholarly works on mills. Their books are now to be found in our ‘Wind and Watermills Collection’.
Matthias Werner (Curation and Discovery Administrator)
This year I have been focused on cataloguing books and cartoons for the British Cartoon Archive (BCA). I’ve catalogued the remaining books from the Eric Linfield Collection. I am currently working on the John Jensen Collection. John Jensen passed away in 2018, and the Special Collections Team has collaborated with his widow, Pat, and sons, Hal and Sean, to incorporate material from his estate into the existing collection at Kent. The books that have been passed on to us are from various eras and countries and primarily focus on caricature, cartoons, and comics.

Das grosse Trier-Buch, Walter Trier (1972)
My personal highlight, however, has been working on a book from our general BCA collection: Cataloguing a book on Walter Trier, a renowned German artist and illustrator, best known for his work on Erich Kästner’s children’s books. Seeing illustrations like the one below brought back some fond memories from my own childhood.
Additionally, I continue to catalogue Steve Bell’s cartoons for the BCA catalogue. Steve has been sending us his works published in The Guardian, ensuring they are preserved in the national cartoon archive. Looking through pieces like the one below takes me back to the surreal and bewildering times of the COVID pandemic.

[No caption], Steve Bell, 04 Mar 2020 (4470-040320 CONVID19)
Emma Solway (Curation and Discovery Administrator)
Ella Baron- Political Cartoonist
The British Cartoon Archive, housed in Special Collections and Archives, is a unique and ever-expanding collection. I have recently started cataloguing cartoons published in the summer of 2024, from a range of newspapers and cartoonists. This is challenging as each artists’ signature caricatures, styles and motifs must be learned and recognised over time. In addition, describing the events satirised within each cartoon involves developing a good knowledge of current domestic and world politics and the significant public figures of the day. This is an interesting and stimulating part of my job, even more so when a cartoonist new to you grabs your attention.

[No caption], Ella Baron, 05 Jul 2024 (115193)
It is still quite rare to see political editorial cartoons drawn by women in my work, so she interested me immediately. The “boys’ club” is a common complaint of women working as cartoonists. As most editorial cartoonists stay in their jobs for life and are historically all men, this leaves women with little opportunity. However, it was great to see Ella’s biography, as she is having a flourishing career working regularly for the Times and the Guardian amongst others, after winning the British Cartoon Associations Young Cartoonist of the Year in 2017. As she once commented she enjoyed making a living from drawing Trump all day, I’ve included one of her cartoons featuring him from the Times in August this year. To learn more about Ella visit
Ella Baron Cartoons.
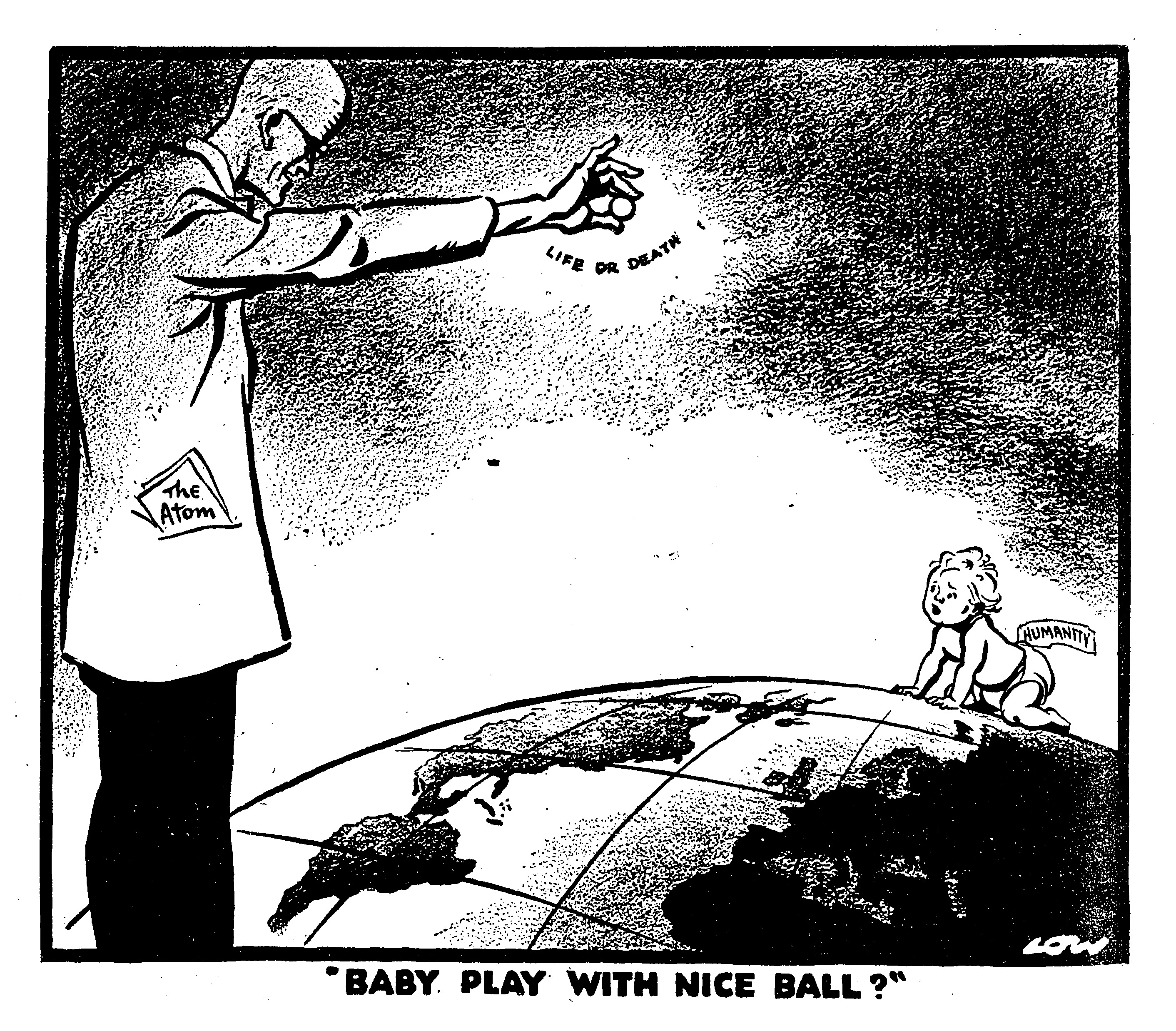









 In Whitehall, crowds awaited Prime Minister Winston Churchill who addressed them from the balcony of the Ministry of Health building. Others gathered outside the Houses of Parliament in Parliament Square, where Churchill’s address was played over loudspeaker.
In Whitehall, crowds awaited Prime Minister Winston Churchill who addressed them from the balcony of the Ministry of Health building. Others gathered outside the Houses of Parliament in Parliament Square, where Churchill’s address was played over loudspeaker.




























