Just like last year, 2021 has been unusual, interesting and busy in equal measure. The Special Collections & Archives team have been working from home, then in a hybrid style, then back to home again as the year has progressed. As the weather takes a turn for the cold and lights turn on ever earlier, we thought we’d use this end-of-term feeling to continue one of our favourite traditions: our highlights of the year!

Karen (Special Collections & Archives Manager):
At this time of year I am always amazed to look back and consider just how much my amazing team have achieved in the past twelve months. We may be in the grip of a pandemic but it has done nothing to impede their dedication and enthusiasm for our collections and the service we run. Well done Team! This year has been one of changes – we have changed the way we work and now operate in a hybrid way dividing our time and our tasks between home and office. There has been a change in the make-up of our team -we were sad to say goodbye to Tom Kennett, University Archivist for over three years but delighted to welcome Beth Astridge, our Project Archivist for the UK Philanthropy, to the post. We also changed our digitisation capability with the arrival of our new digitisation equipment – thank you to UKRI AHRC Capability for Collections funding – you will be able to see the results of this in 2022.
One of the huge advantages of hybrid working is that people have been able to take advantage of working from home to spend time on processing digital collections and digital preservation. The fruits of this labour are highlighted below by Rachel, Alex, Emma, and Mandy. We now have many of our great photographs catalogued and available online (shh don’t tell anyone… but my favourite is Bag Puss in his cap and gown!) and the University’s audio collections are being digitally preserved for posterity. Steve Bell’s digital cartoons are being catalogued from Emma’s home office and they are taking her back in time to the world BC (before Covid). Clair has taken full advantage of our new way of working and has catalogued a hybrid collection while hybrid working. The Meredith papers are now available via our online catalogue and they are definitely worth investigating.
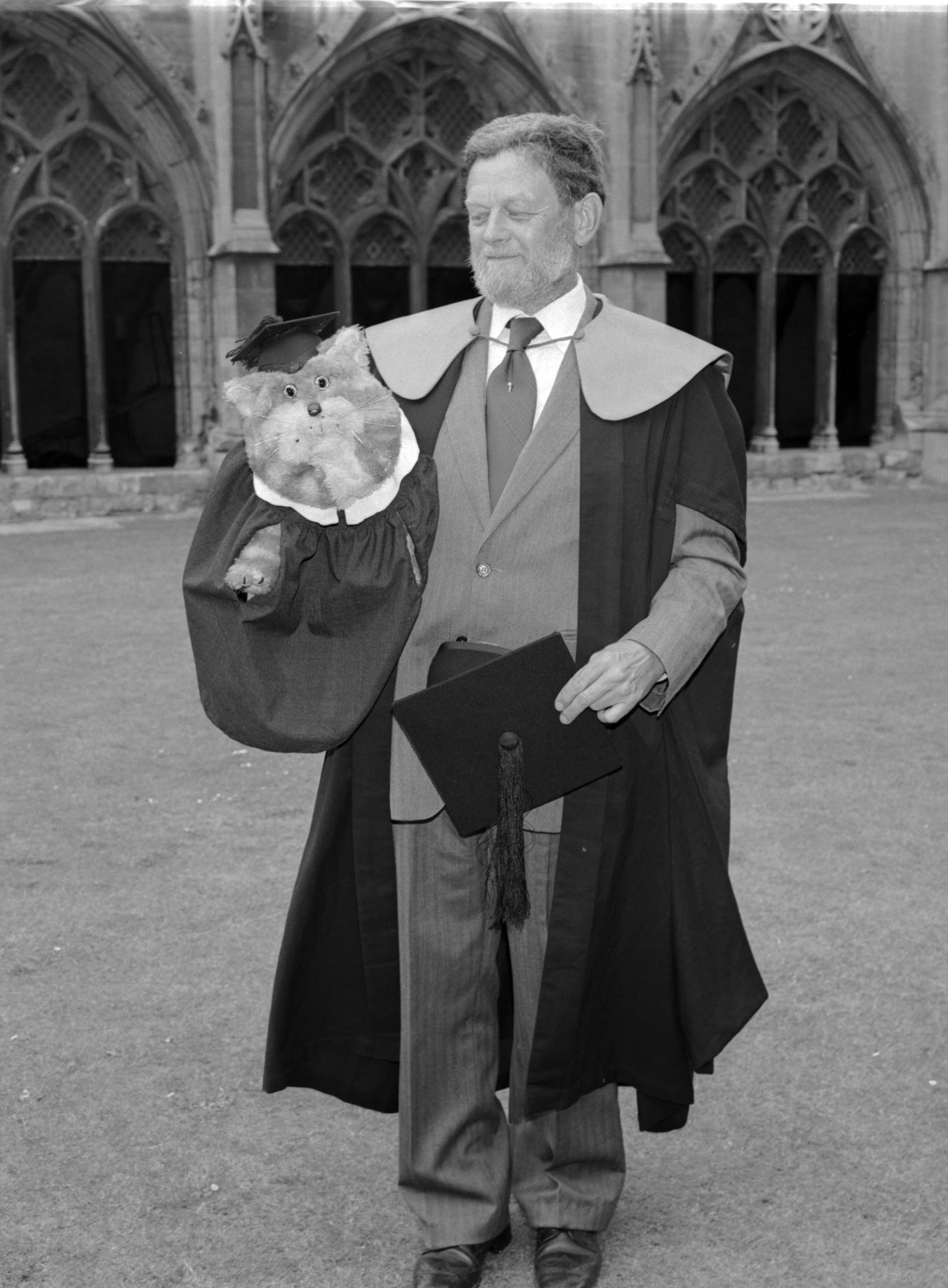

UKA/PHO/1/1488: Peter Firmin and Bagpuss in the Cathedral getting an honorary degree
It has also been great to be working on campus again and Jo and Christine (our Honorary SC and A assistant) will be telling you about the exciting things they have been getting on with including developing new seminar sessions and researching and selecting unique costume designs from the Drummond Pantomime collection for display in the Templeman Gallery. Beth has spent most of this year consolidating the work she has been doing in developing the UK Philanthropy Archive and will continue to oversee the collection development in the coming year. And speaking of the coming year, we will be working on plans for 2023 when we will celebrate 50 years since the first cartoon collections arrived at the University – watch this space…!

Rachel (Metadata Assistant, Collections Management):
“This year I embarked upon the enormous task of cataloguing the thousands of official University of Kent photographs in our University Archive, all of which are digitised and being added to the website as I catalogue them.
As a former student here at Kent and a member of staff for seven and a half years it’s been really interesting to see how the campus has changed from the mid sixties to the present day, but my favourite thing about these images is researching the people in them, and finding out stories of former staff and students (and admiring old hairstyles and fashions).
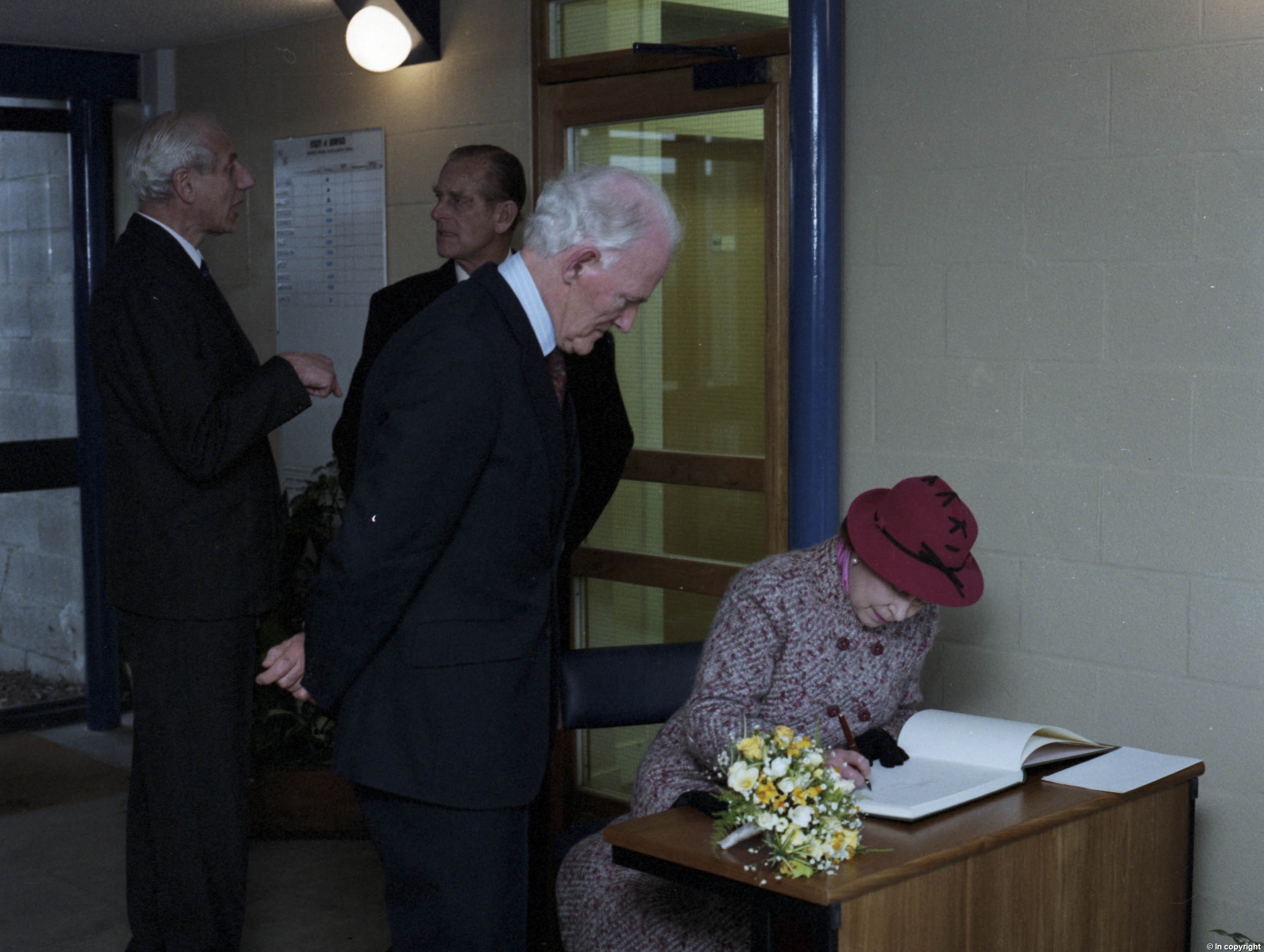

UKA/PHO/1/1465: Queen signing the University visitor book when she and Philip came to open the Cornwallis extension (the Octagon)
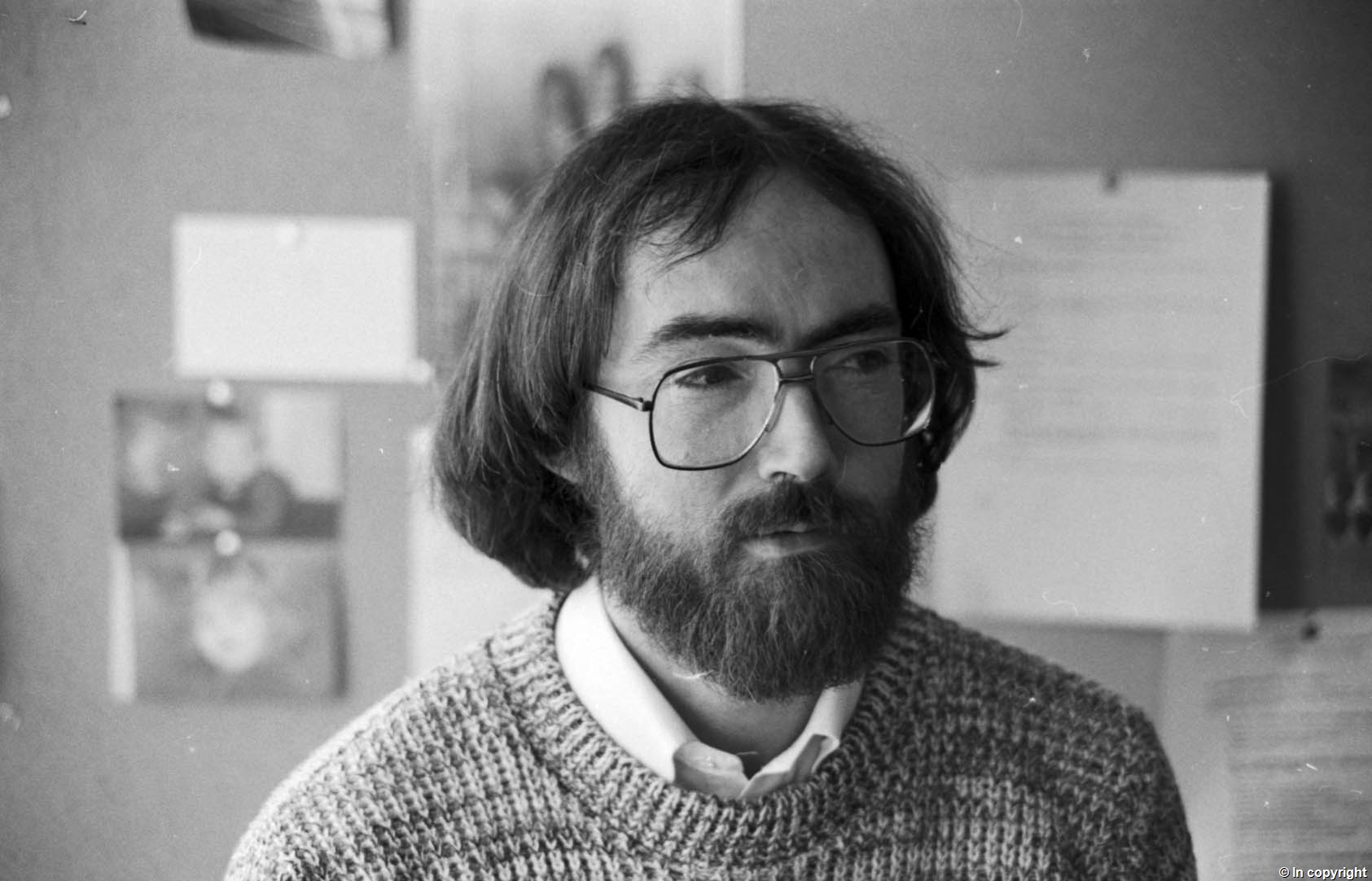

UKA/PHO/1/1370: Professor Peter McGill who identified himself when I asked if it was him and gave me other names
Identifying staff is difficult so I am indebted to the former staff network and those academics I have contacted directly who have supplied me with names and job titles when I’ve needed them, but also with extra information about old university structures, events and even on one occasion golf handicaps! I’ve still got several thousand to keep me busy next year, and I’m looking forward to it!”
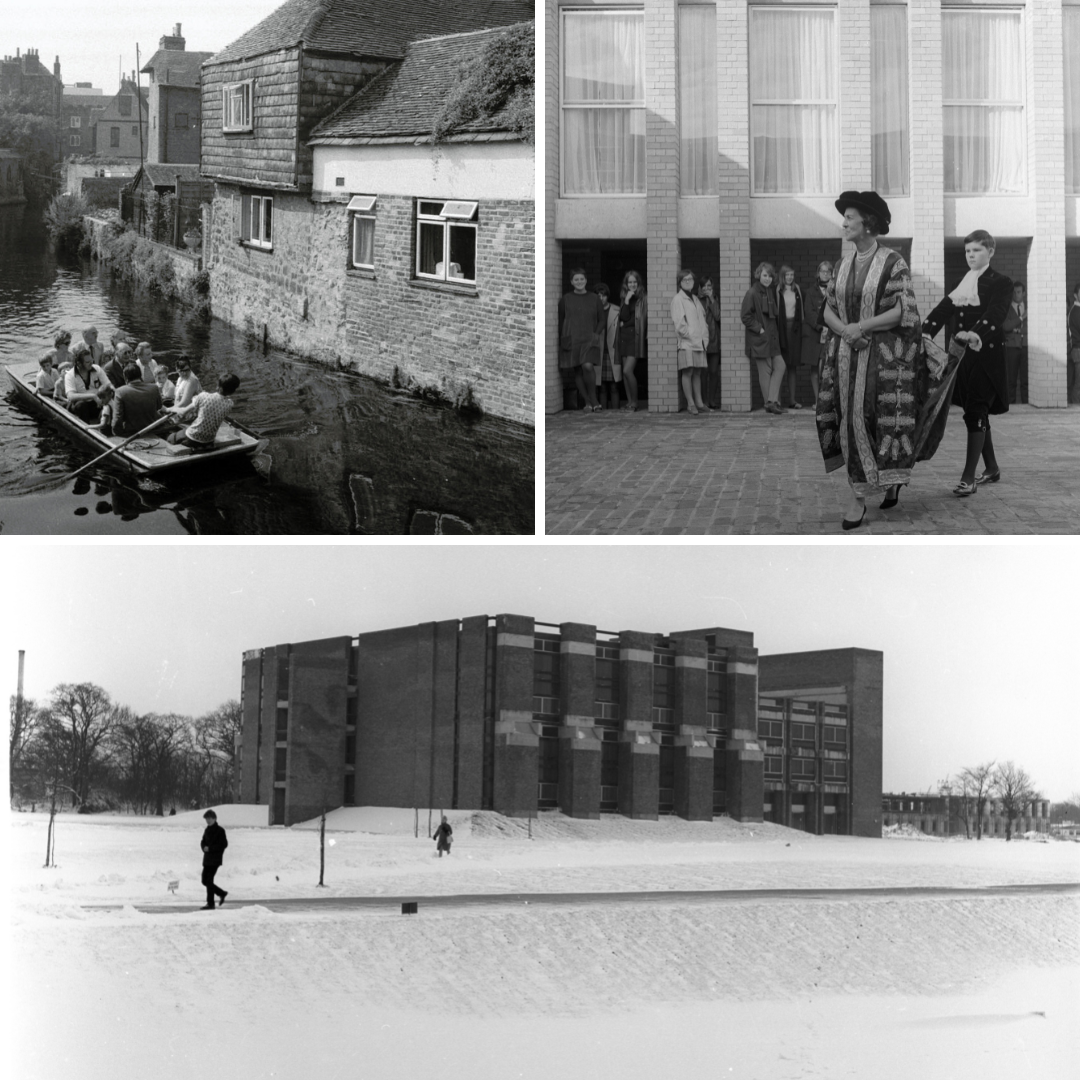

(Clockwise L – R): UKA/PHO/1/620: Stour River tours!, UKA/PHO/1/122: Duchess of Kent leaving the first graduation ceremony in Eliot Dining Hall, complete with page boy, UKA/PHO/1/140: Snow around the original Library
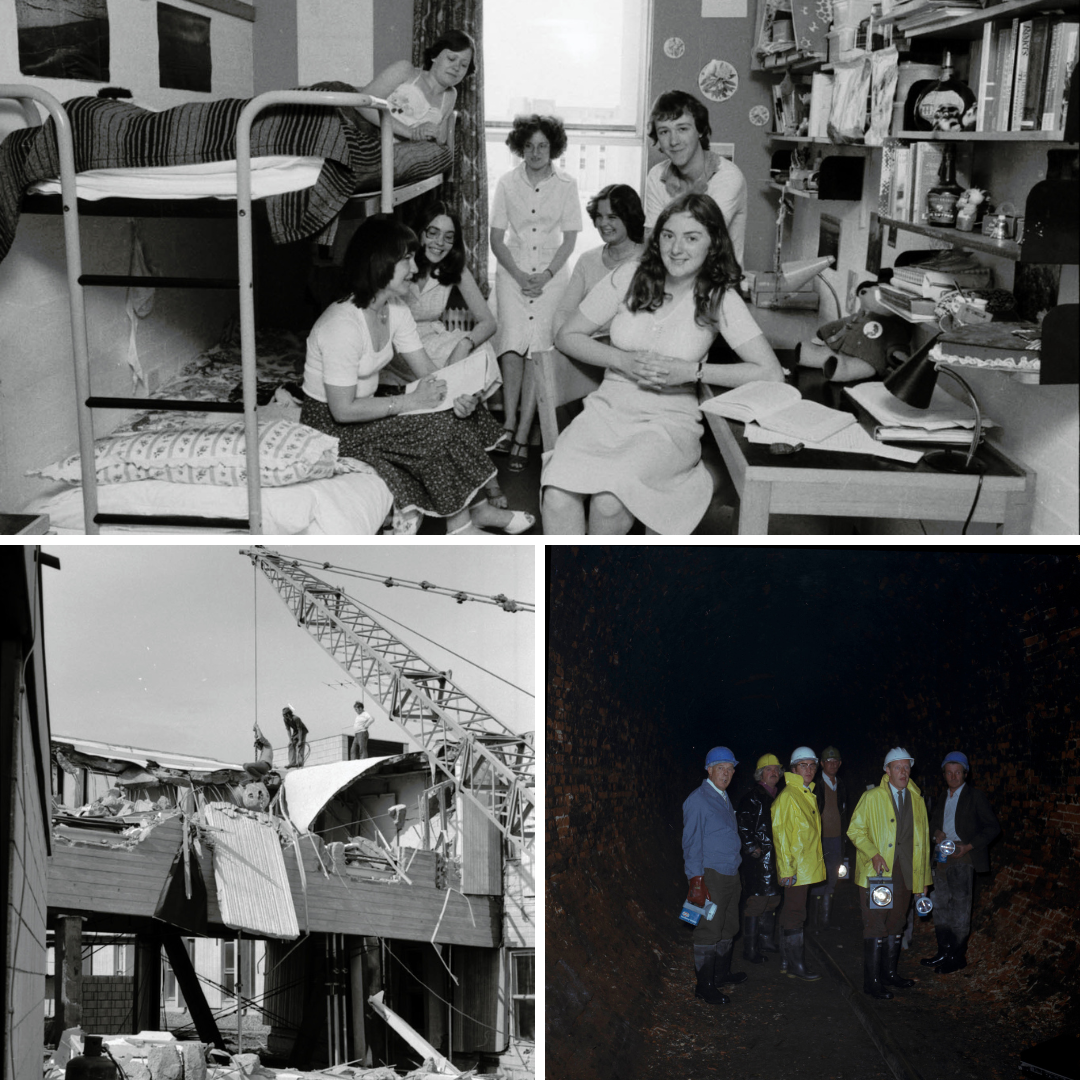

(Clockwise L – R): UKA/PHO/1/1157: 70s college bedroom, AKA Paddington Goes to University, UKA/PHO/1/807: Standing in the railway tunnel after the collapse beneath Cornwallis, UKA/PHO/1/747: Demolition of the corridor between Gulb and Cornwallis following the collapse of the railway tunnel

Jo (Senior Library Assistant – Special Collections & Archives):
“For me, 2021 has been a lesson in appreciating my role and the many opportunities I get to introduce students to our beautiful collections. We welcomed groups back into our seminar room from September and gosh I’ve missed facilitating these sessions.
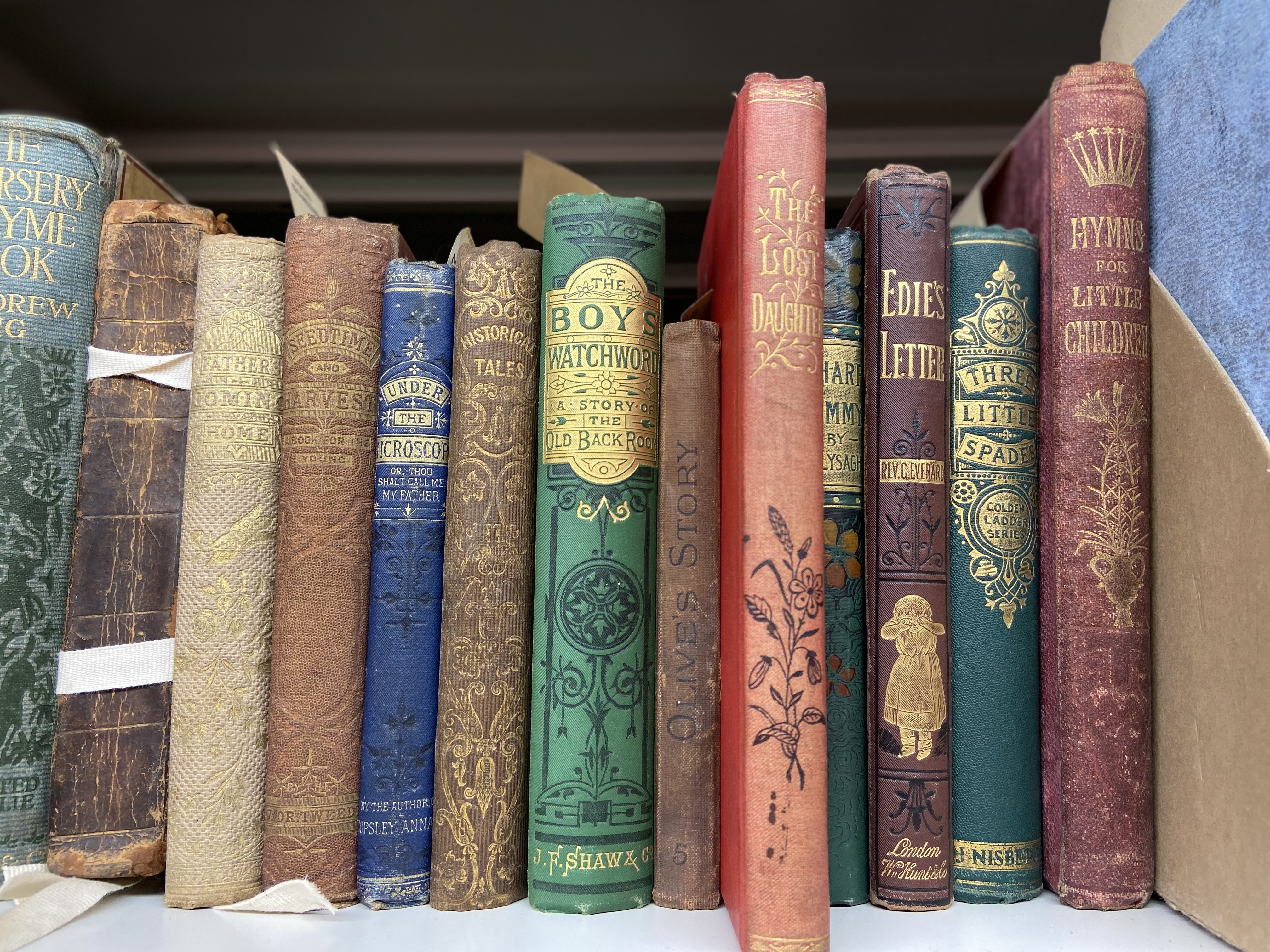

Colourful Victorian children’s literature books in our stores!
Particular highlights include the energetic reactions of Drama undergraduates when looking at material from our British Stand-Up Comedy Archive (“this is SO COOL! I’m having an out of body experience!”) and working with students from Canterbury Christ Church University for the very first time. The latter involved finding material from our collections relating to Victorian children’s literature which was honestly such a treat for me.

A tiny book found in our Victorian Children’s Literature collection, containing a poem for every day of the year
I’ve also been leading on supporting University Open Days for the School of English, where we meet prospective students (and their parents), get them interacting with our material and chat about what it’s like to study at Kent. We’ve had some really positive feedback for these events and I’m looking forward to supporting Applicant Days next term for both English and History students.

Display of SC&A items for potential University of Kent English students, October 2021
On a non-outreach note, I’ve been working with Clair and our Marketing Team this year to design and update the SC&A website which should be going live in the near future. This has involved a huge range of work, from making the site a lot more visual to rewriting outdated biographies and creating new areas for our digital resources. It’s been a lot of fun and we can’t wait for you to see the results soon!”
 Alex (Digital Imaging Assistant – Collections Management):
Alex (Digital Imaging Assistant – Collections Management):
“Despite the Pandemic and subsequent Lockdowns, I have been able to set up an effective Audio Cassette Digitisation Station at home. So, throughout these strange times, both at home and in the hybrid working environment, I have continued to digitise the University’s collection of recordings made on vulnerable analogue magnetic audio tape. I’ve now completed the digitisation of the entire series of University Open Lectures, T.S. Eliot Memorial Lectures and Keynes Seminars. This totals almost one thousand individual recordings dating back to the late 1960s.
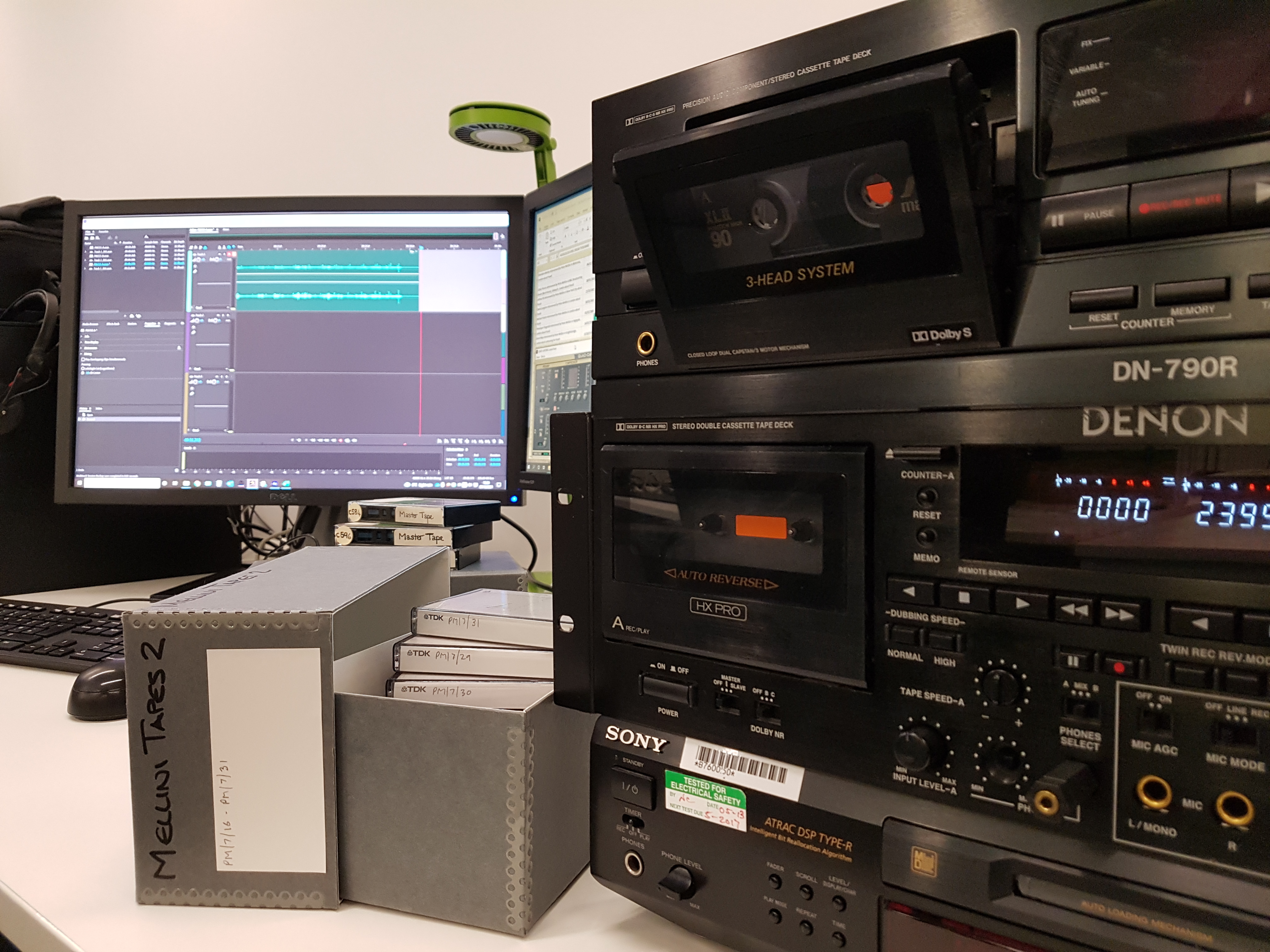

Alex’s Hybrid Working setup
Following on from this I have moved on to the Audio Cassette recordings which form part of the British Cartoon Archive. These mainly take the form of unique interviews with cartoonists (ranging from Charles Schulz to Steve Bell) carried out by Keith McKenzie and Peter Mellini.

New photographic equipment being set up!
In addition, with grateful thanks to a generous external grant, we now have a recently installed photographic reproduction rig equipped with a state-of-the-art high-resolution camera. This set-up will enable us to digitise both flat artwork and 3D objects within the archive collections to an optimum level. I have been working with my colleagues Matt and Clair to develop efficient digitisation workflows with this impressive new equipment.”

More shiny new photographic equipment in its new home

Matt (Digital Imaging Team Leader):
“[Following on from our AHRC grant. which enabled us to invest in amazing new reprographics hardware] we have been progressing with testing the new Phase One digitisation equipment.
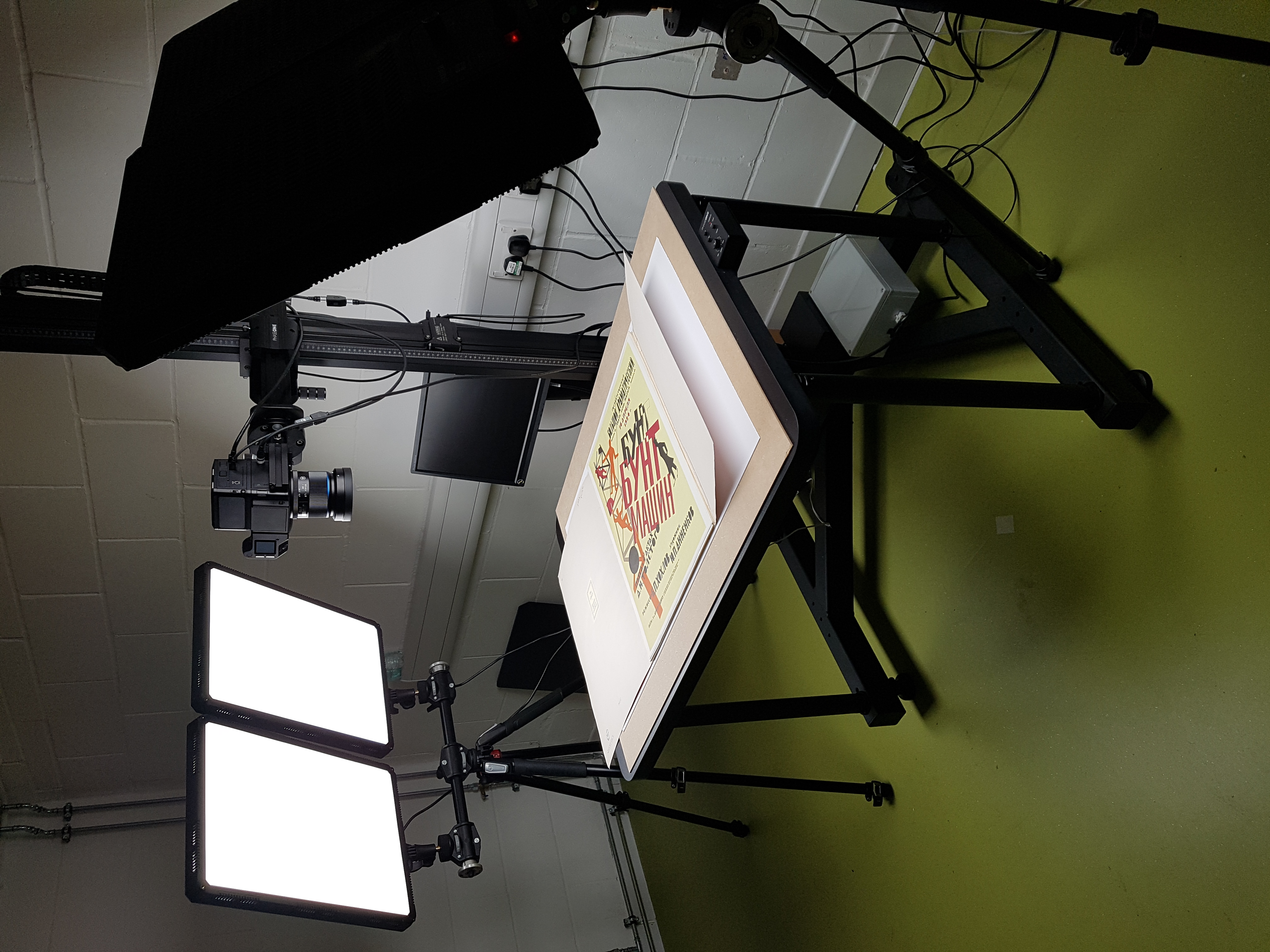

The rig setup for our new reprographics equipment
We have been practicing use of the equipment using material in various formats and have been collating questions to discuss with our contact at Phase One in the coming weeks. We will continue to develop our workflow, ready to begin our first large scale project (the Beaverbrook Collection) in 2022.”

Beth (Project Archivist: UK Philanthropy Archive, January – November and University Archivist, November – present):
“It is always a bit of a treat to look back at the year just passed and celebrate all the achievements and exciting things that have taken place, and 2021 has been no different. It turned out to be a very busy year for the UK Philanthropy Archive! A key achievement was that we were able to host the inaugural Shirley Lecture in May (delivered online) – where Dame Stephanie Shirley CH delivered a fascinating lecture giving us an insight into her life and how it influenced her philanthropy.

Annual reports from the FI Group – the software company started by Dame Stephanie Shirley
I was able to spend some time listing and cataloguing both the Shirley Foundation collection, and the collection of Amanda Sebestyen – both the catalogues will both be available in early 2022. Amanda Sebestyen is a human rights journalist and activist, and looking deeper at her archive has revealed a fascinating collection relating to her family settlement trust and the challenges of closing it down in order to donate the proceeds to ethical charitable causes in Australia. Some great research potential there!

Postcards and press release from a project called ‘Sea of Hands’ in Australia funded by the family settlement of Amanda Sebestyen as part of her focus on supporting native and indigenous people
We were really pleased to receive the archive collection of the Marc Fitch Fund in September. The fund was set up in 1956 by Marc Fitch with a focus on supporting publishing work on local history, genealogy and heraldry, and we are cracking on with getting this interesting collection catalogued and available for use.

Coat of Arms for the Marc Fitch Foundation – awarded in 1979 in recognition for their support for heraldry and genealogy research

Close up of the Marc Fitch Fund Coat of Arms
In November I was delighted to attend the 50th anniversary celebration of the John Ellerman Foundation. It was brilliant to hear all about the ongoing work of the Foundation and the research taking place to explore their history. We have been working with the Foundation and have supported a project to translate 200 letters written in Afrikaans by John Ellerman as part of their history project, and we are looking forward to further collaboration in 2022!
At the end of this year I was also delighted to accept the post of University Archivist within Special Collections & Archives, so I can now look forward to continuing work on the philanthropy collections as well as the wider University Archives, so 2022 looks like it will be just as busy as 2021.”
 Emma (Metadata Assistant, Collections Management):
Emma (Metadata Assistant, Collections Management):
“The British Cartoon Archive, housed in Special Collections and Archives, is a unique and ever expanding collection. Steve Bell, a well-known cartoon satirist, has produced cartoons for the Guardian for many years. Steve has deposited many digital copies of his cartoons with us and I have recently begun cataloguing these.
Sometimes it is hard to remember life before Covid, but I have suddenly been hurled back to the pre-Pandemic political arena of 2018 and it has been a welcome break from the issues we face at the moment. Steve has specific ways of characterising his political figures and I have had fun learning who is who. Teresa May always wears leopard sprint shoes and appears dressed as a clown and Donald Trump often has the top of his head in shape of a toilet seat!
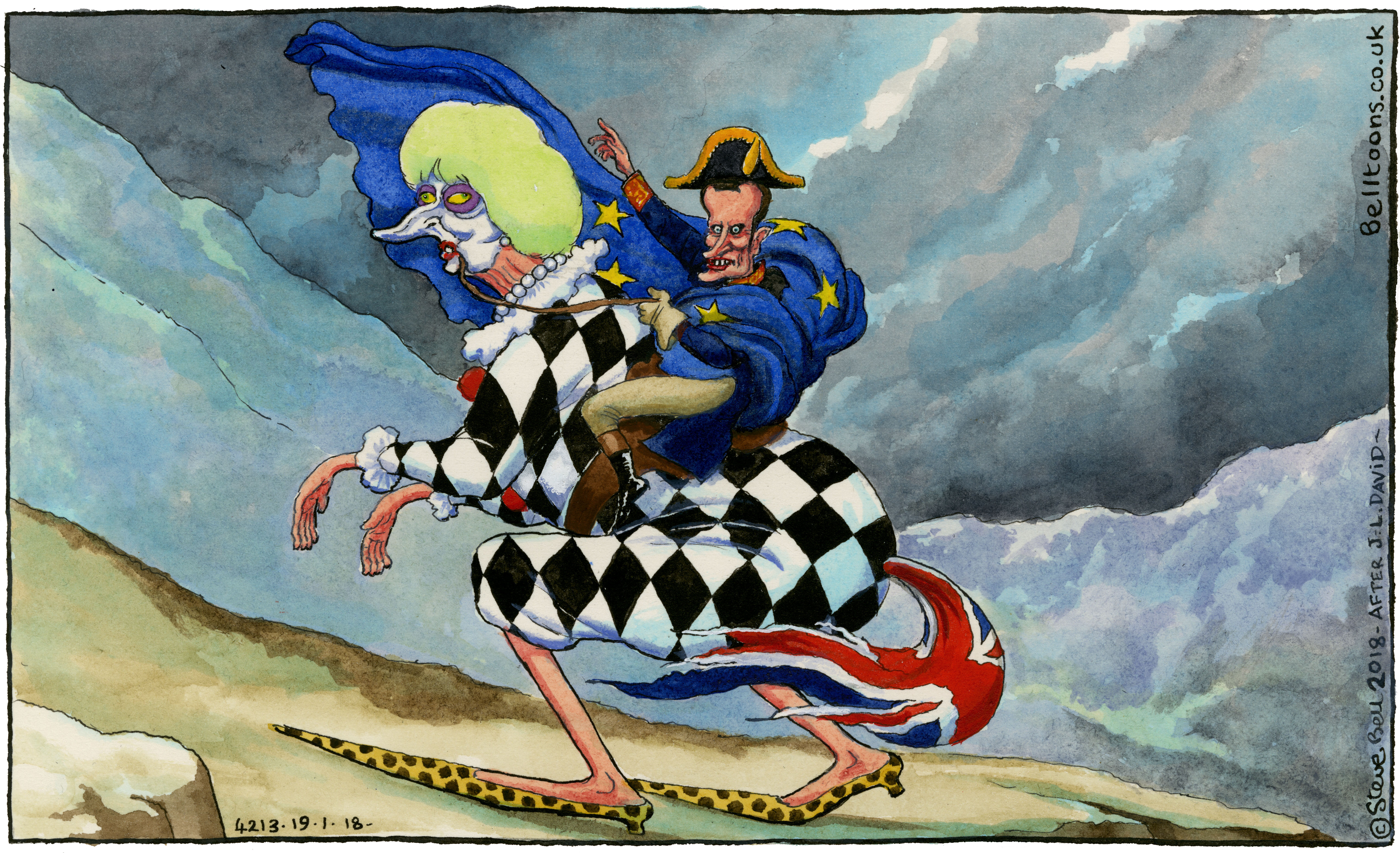

SBD1892: French PM Macron riding on Theresa May
Copyright Steve Bell 2018/All Rights Reserved
Describing the events satirised within each cartoon involves using the subject hints Steve has embedded in his metadata (thank you Steve) to investigate what was happening in politics that day. This cartoon of Teresa May and Emmanuel Macron is one of my favourites so far.”

Mandy (Library Assistant – Digital Imaging):
“I have had the great job this year scanning photos of Canterbury from the Blitz to the City wall.

Canterbury being rebuilt after the Blitz! Canterbury Photographs Collection, LH/CANT/PHO
It has been so interesting [to see] how Canterbury has changed over the years.”

More post-war building work. Canterbury Photographs Collection, LH/CANT/PHO

Christine (Library Assistant – Learning Environment):
“‘Tis the season to be jolly –
The pantomimes I grew up with were a garish, bolshy composite of slapstick, sequins and sweeties, a night of misrule where hyperactivity was encouraged, Schadenfreude was permitted, and a happy ever after was guaranteed. I remember sets designed like candy shops, and ‘dames’ trussed up in ridiculous frocks. I remember catching a toffee tossed to the crowd, and ‘he’s behind you’ being yelled out. There was something magical about lines that rhymed, and watching a show well past bedtime!

Costume design for Robin Hood, David Drummond Pantomime Collection

Costume design for Maid Marion in Robin Hood, David Drummond Pantomime Collection
Now that I’m older, magic is harder to find, but these pantomime costume designs from SCA’s David Drummond collection come pretty close. From 1880s-1950s, this collection holds examples by Archibald Chasemore, Antonio Comelli, C. Wilhelm and Doris Zinkeisen (amongst others). The collection also represents important aesthetic and cultural shifts that played out in the theatre, from the imperial appropriation underpinning the exotic spectacles of the late Victorian stage to the fanciful historicism of the mid-20th century, where medieval romance or Rococo chic transported the audience to a bygone realm. Just consider the bizarre Chinoiserie dominating Wilhelm’s 1889 Aladdin, and the contrasting merry olde England of Zinkeinsen’s Babes in the Wood (1956).”
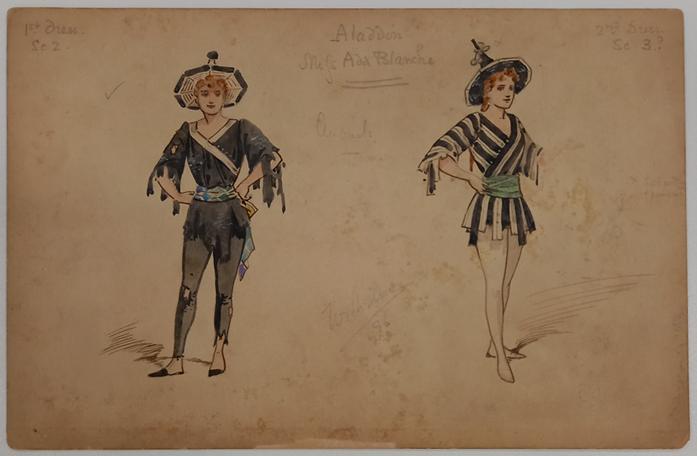

Costume designs from Aladdin, David Drummond Pantomime Collection
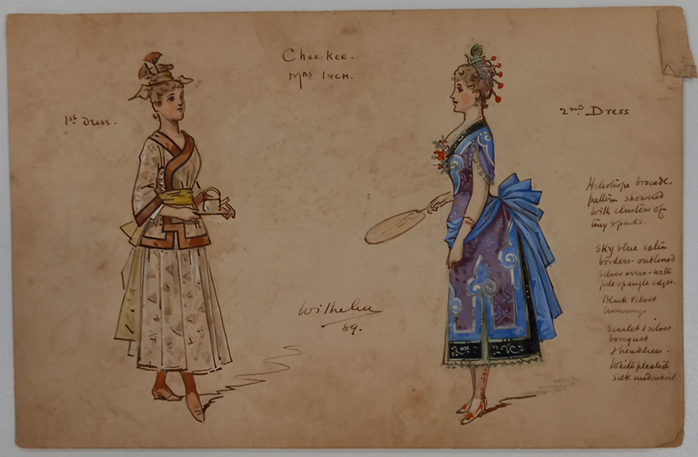

Costume designs from Aladdin, David Drummond Pantomime Collection
 Clair (Digital Archivist):
Clair (Digital Archivist):
“It’s been another year of change and adaptation for many of us. Whilst at times challenging, we’ve also seen some positive outcomes of this change in Special Collections and Archives. A personal example of this positivity for me was the opportunity to catalogue a hybrid collection (by which I mean a collection of both physical and digital materials) of research papers related to the Meredith Family of Leeds, in Kent, called the ‘Sir William Meredith Research Collection’. Working both on campus and from home, the nature of this hybrid collection provided the opportunity to carry out this work in both locations.
Miriam Scott, a retired teacher and family historian, was inspired to research the Meredith family after admiring the Meredith Memorial at St Nicholas Church near her home at the time in Leeds.

Meredith memorial, MER/1/2/32-D
Scott used documents and books from a number of libraries and records offices during her research, including the Public Record Office (now The National Archives), the British Library, and Leeds Castle Archives. The research led to an article being published in the Friends of the National Archives magazine entitled ‘Sir William Meredith, knight. A gruff Welsh voice in London’. Professor Catherine Richardson in the Department of Medieval and Early Modern Studies (MEMS) at the University of Kent, supported the deposit of the research papers.
Sir William Meredith ([1560?]-1605) was a knight and Treasurer at War during the reigns of Queen Elizabeth I and King James. His family lived at what was Leeds Abbey in Kent, from around 1608-1758.
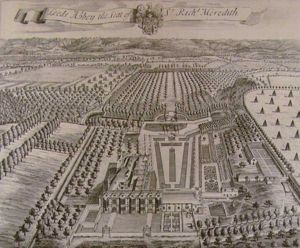
Leeds Abbey historic view, 1719
The Abbey was built on the site of the former Leeds Priory, which was left in ruin after the dissolution of the monasteries by Henry VIII in the early 1500s. Sadly, nothing remains of the Priory buildings today, and the only remains of the Abbey are the ruins of the pigeon house and the Slype. The site is located near Leeds Castle.
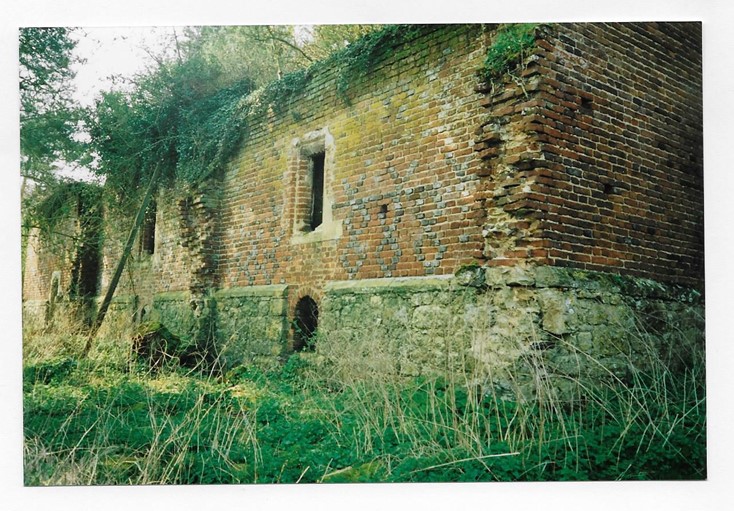

Remains of the pigeon house, MER/1/2/8-D
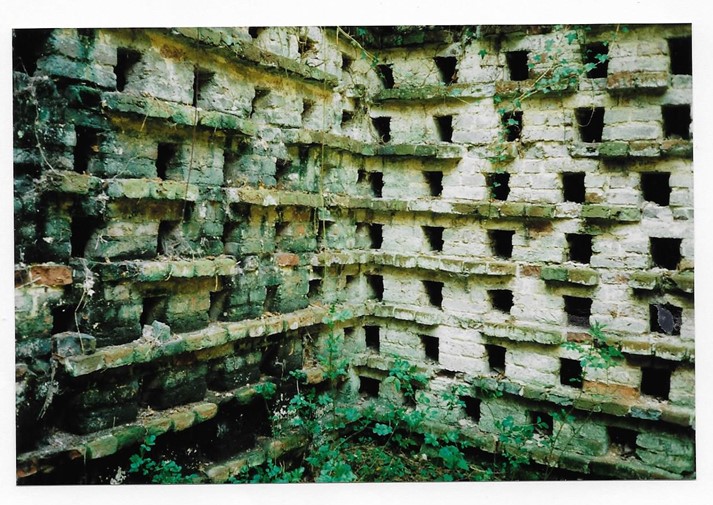

Remains of the pigeon house, MER/1/2/8-D
The Merediths were a well-established family of Denbighshire, Wales, with a branch of the family remaining there until at least 1901. The research includes information regarding the history of Leeds Abbey, the families of Sir William Meredith’s children (including the Cottington and Wyche families), as well as his connection to family in Denbighshire, North Wales. If you’d like to see any of the material, please let us know at specialcollections@kent.ac.uk.”
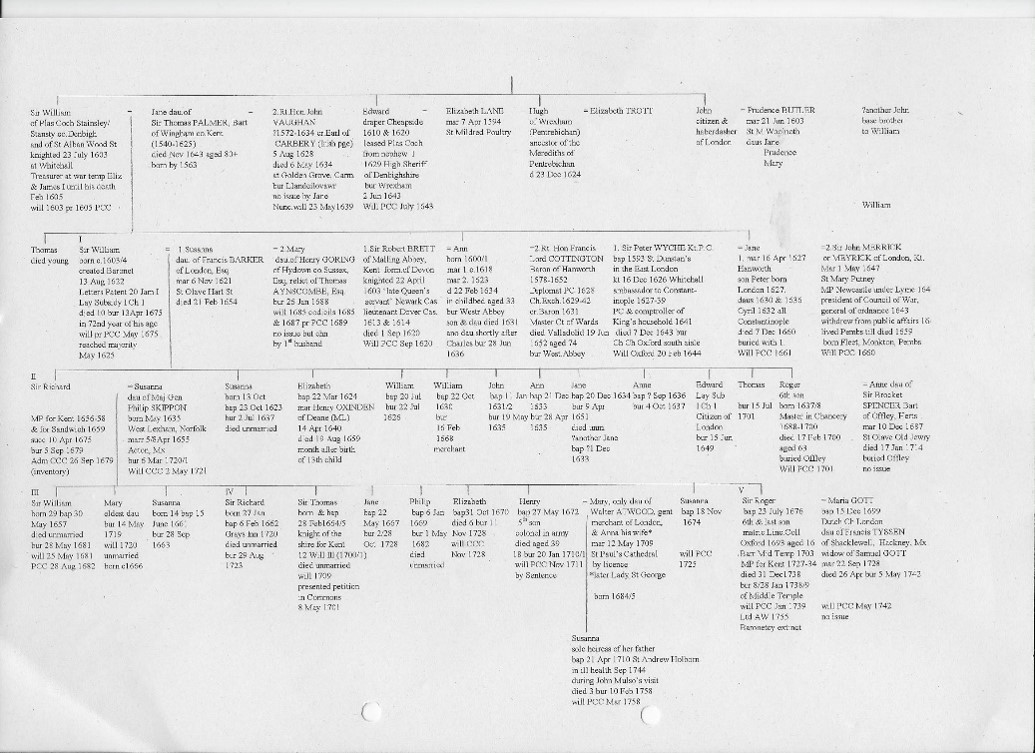
Meredith family tree, MER/1/2/27-D

The SC&A team wish you a very happy Christmas and New Year; we hope you can rest and spend time with loved ones. We’re closed for Christmas from Friday (17th December) and will be back in the office from Tuesday 4th January 2022. Our Reading Room will reopen at the start of term (week commencing 17th January 2022).