February 11 is the International Day of Women and Girls in Science. To commemorate this occasion, we’re going to delve back into our Maddison collection to see how women have been involved in sciences from the very beginning. Today let’s take a look at Mary Anne Atwood, who was afraid she had revealed one scientific secret too many…
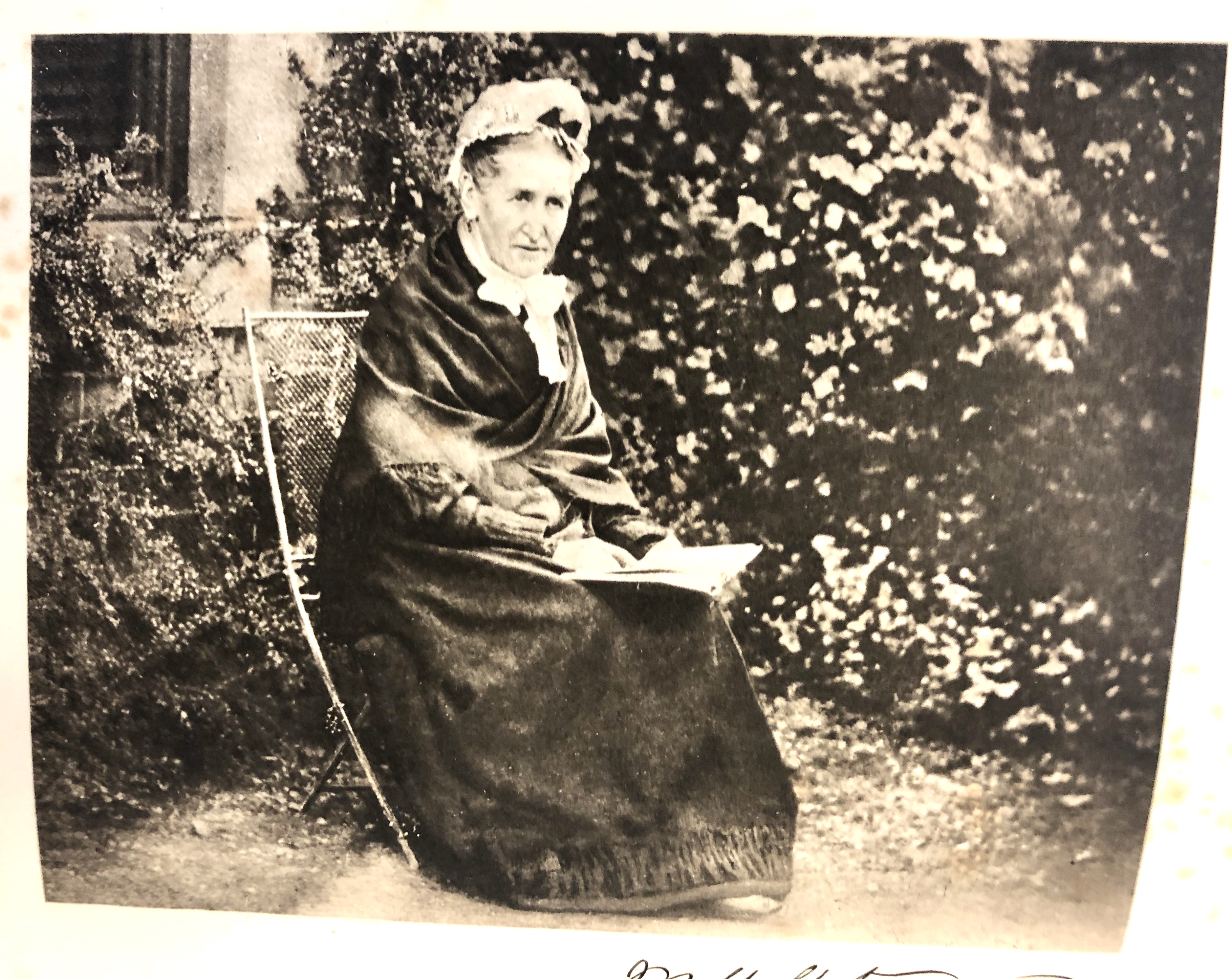

Photograph of alchemical researcher Mary Anne Atwood, undated.
Who was she? Born in Dieppe in 1817, Mary Anne Atwood (nee South) grew up surrounded by her father’s books in Gosport, Hampshire. Like many women of the era Mary Anne received no formal education but learnt Latin, Greek, and the classics at home. Encouraged by her father Thomas South she joined a circle of theosophists; a religious group who believed that spiritual knowledge was held in a group of individuals known as the Masters. It was this circle that sparked her research in alchemy.
What did she write? In 1846 Mary Anne and her father released a book detailing their thoughts and research so far: Early Magnetism in its Higher Relations to Humanity as Veiled in the Poets and the Prophets, under the pseudonym Thuos Mathos. The work was well received and the praise encouraged the Souths to begin a much bigger project: a full explanation of the purpose and methods of the alchemical process.
What is alchemy anyway? Today, we know alchemy as the discipline of trying to turn lead into gold, practised between the 16th and 18th centuries. However during the 19th century, as it became more widely recognised that this was not possible, alchemy as a discipline took on a more spiritual slant. Researchers began to examine the relationship of mankind – and the soul – to the wider cosmos, exploring if it was possible to refine the soul away from the influences of the external world and society back to a state it would have been in when God created it. This branch of alchemy is known as Hermetism (or Hermetic writings) and it is this that Mary Anne Atwood and her father were interested in, rather than the Philosopher’s Stone story we know from J.K. Rowling’s world today.

Contents page of Atwood’s work ‘ A suggestive inquiry into the hermetic mystery : with a dissertation on the more celebratedof the alchemical philosophers, being an attempt towards the recovery of the ancient experiment of nature’. Long title, fascinating book.
Why has she not become more famous? In 1850, Mary Anne published A Suggestive Inquiry into the Hermetic Mystery which was the culmination of years of research into spiritual alchemy. The work was supposed to be published alongside a poem written by her father, The Enigma of Alchemy. When A Suggestive Inquiry… was published it had not been read (or edited) by Thomas South, and shortly after its release to the world the Souths decided it was not fit for sale and withdrew the book along with most existing copies (to the ire of their publisher). The reasons for this withdrawal are twofold. Firstly (and most importantly) Mary Anne and her father believed that they had explicitly written about secrets that should have stayed hidden within allegorical texts, and that this knowledge could be dangerous if in the wrong hands. Secondly there is a suggestion that Thomas South became more devoutly religious between the writing of the texts and that this prompted a change of heart about the matter.
Following A Suggestive Inquiry…‘s withdrawal, Mary Anne retreated from alchemical society. In 1859 she married Reverend Alban Thomas Atwood and lived a very quiet life in Yorkshire. After her husband’s death in 1883, there is some evidence that Mary Anne was approached about a possible reprint of A Suggestive Inquiry… and whilst she did not wish to see it in print again – for fear of it being reproduced and sold without her consent – she gave a few copies to friends and made some minor amendments to the text itself before her death in 1910.
Why is she important? A Suggestive Inquiry into the Hermetic Mystery is the first work that gives a comprehensive insight into alchemy as a discipline, and consequently Mary Anne’s work is vital for establishing this particular area of historical scientific research. In 1918 it was republished by Mary Anne’s friend, the painter and thinker Isabelle de Steiger, for the first time since it was withdrawn from sale in 1850.

Title page of the new 1918 edition of Atwood’s work ‘A Suggestive Inquiry…’
Freemason Walter Leslie Wilmshurst, who wrote an extensive introduction in the new edition, suggested that the societal and spiritual impact of the First World War led to increased interest in alchemy and Hermetic writings:
“It was not, I think, the destiny of such a treatise as this to perish at its birth, but rather, when the time should be more ripe for it, to re-emerge from its obscurity and assert that influence which its great merits are capable of exercising. With that clear, sure prophetic vision with which its writer…penetrated the tendencies of modern world movements and conditions, she discerned the impending catastrophe to human society and institutions through which we are now passing.” (p.64)
The copy of Mary Anne’s work we hold is the 1918 edition, which contains additional quotes by the writer. It was collected by the writer and librarian R.E.W. Maddison for his ongoing collection of books relating to the history of chemistry and physics, within which there are many books about alchemy. Whilst the language of Hermetism appears somewhat obtuse by today’s standards, Atwood’s work is a fascinating summary of alchemical studies – and a solid testimony that there are many ways to discover the world beyond traditional education.
Bibliography and further reading:
Mary Anne Atwood, A suggestive inquiry into the hermetic mystery : with a dissertation on the more celebrated of the alchemical philosophers, being an attempt towards the recovery of the ancient experiment of nature. William Tait, 1918. University of Kent Special Collections & Archives: Maddison Collection 19A15.
R.A. Gilbert, ‘Atwood [née South], Mary Anne’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, 2004. DOI: https://doi-org.chain.kent.ac.uk/10.1093/ref:odnb/53866
Robert P. Multhauf and R.A. Gilbert, ‘Alchemy’, Encyclopaedia Brittanica, 2019: https://www.britannica.com/topic/alchemy.
Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island holds the majority of material by Mary Anne Atwood in its Special Collections department.
As ever, more information about the Maddison collection and visiting us can be found on our website.