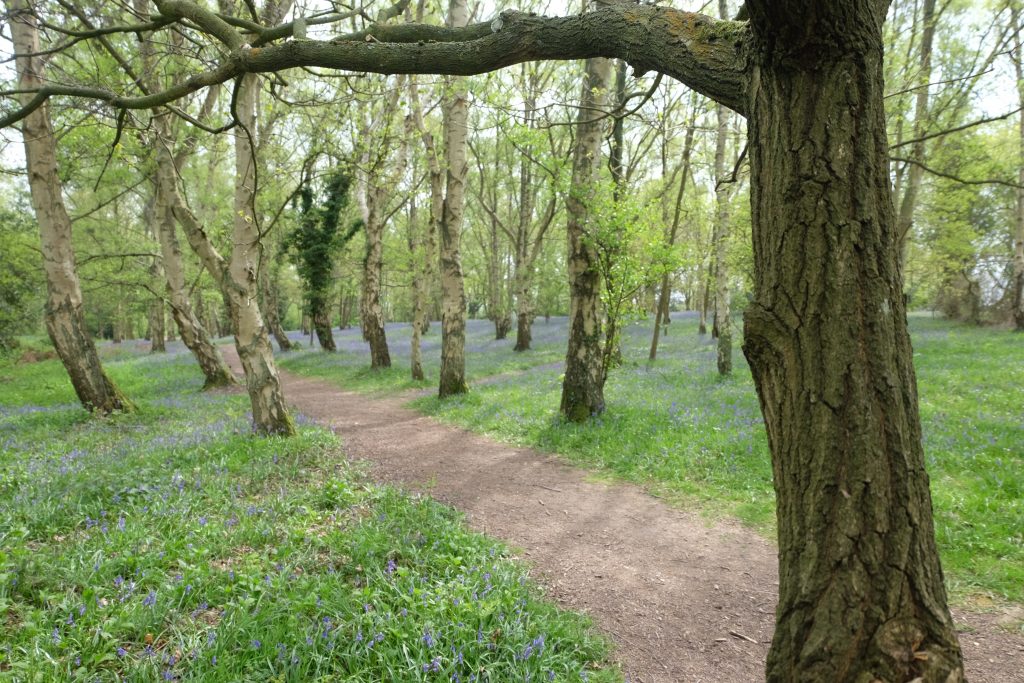
Last year the University took part in No Mow May on central campus for the first time. This means central lawns that would normally be cut were left to grow throughout May.
The main objective was bring landscape management for biodiversity to the centre of campus to raise the level of consciousness about biodiversity issues. Often biodiversity projects are pushed to the outskirts of central campus where the majority of the University community never see them. By bringing No Mow May onto central campus we would be put biodiversity action right in front of people.
Our secondary objectives were to seek a boost in vegetation and invertebrate diversity on central campus in line with the national No Mow May findings; and we wanted to test the assumption that we would face a lot of resistance to a project like this where we would be changing how central campus looked and the expectation for it to look neat and tidy.
No Mow May is Plantlife’s annual campaign calling on gardeners and landowners to leave the mowers in the shed and allow flowers to grow. May is a crucial month for flowering plants allowing them to get established and provide nectar for pollinators and other invertebrates. Just 8 dandelion flowers are enough to produce the nectar sugar needed by a bumblebee each day.
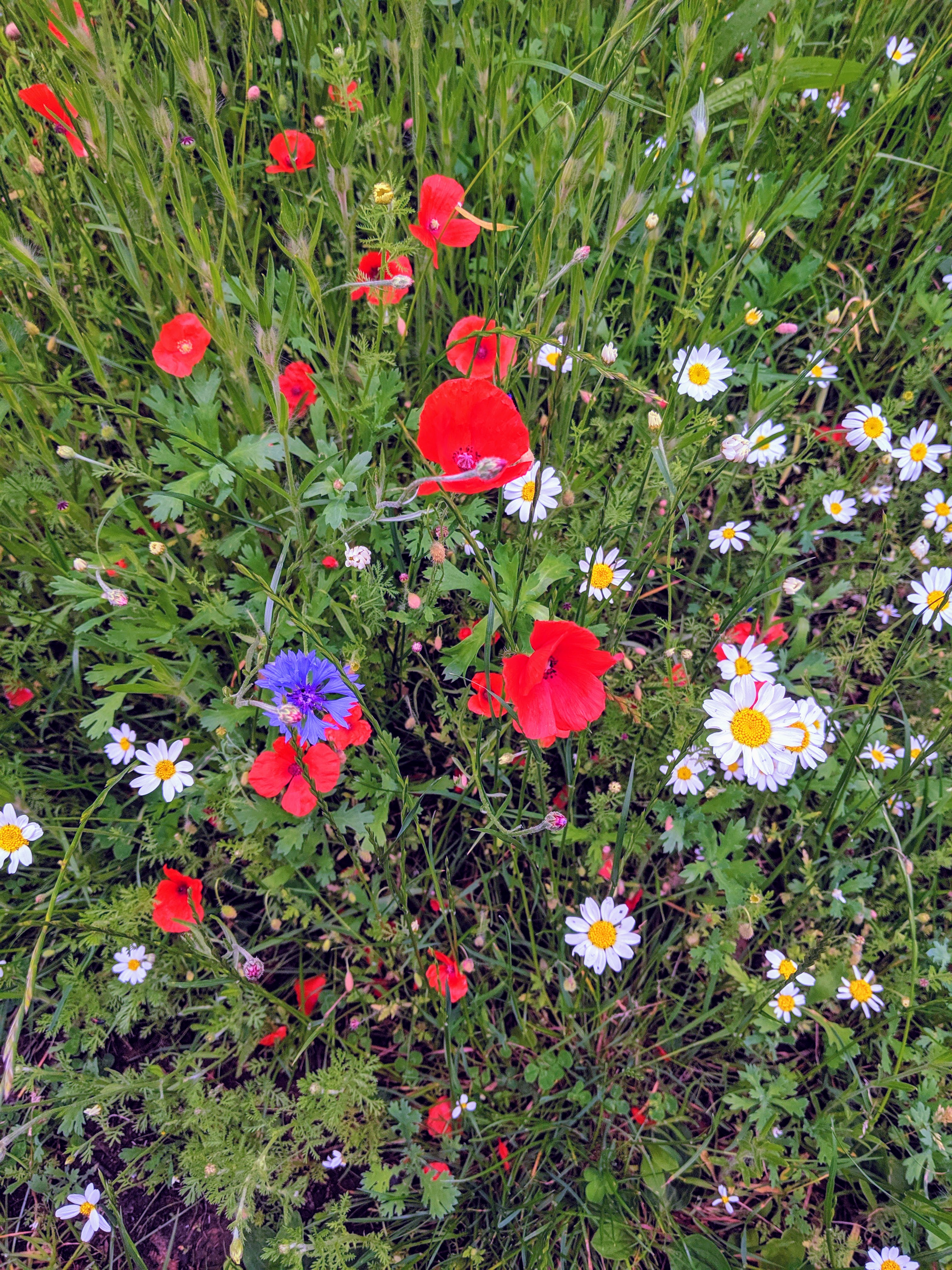

We already leave large areas of our grasslands throughout Spring and Summer as hay and wildflower meadows. We have publicly available plans on our grassland management and future plans for boosting the diversity of these existing meadows. No Mow May goes beyond this in asking people to leave traditionally mown lawns throughout May to boost the available food for pollinators and other invertebrates in this specific time. These lawns are amenity lawns that are usually mown fortnightly throughout this period.
Engaging Students
With the project being so visible we sought to engage students to use their skill sets and apply them to this on campus project.
Conservation students were asked to used their surveying skills to collect data on species richness over the course of the project, and the Conservation Society took this on as an extra-curricula activity.
The signs that communicated the project were created by a Graphic Design student from KSAP as part of their Learning Enhancement Week. A group of graphic design students were briefed on the biodiversity crisis facing invertebrates, what No May was and what the University would be doing. They then produced a series of designs with the winning design being placed around central campus. The signs included a QR code allowing people to find out more and provide direct feedback to the project.

Feedback
We received feedback through three predominant channels: direct emails, submissions through the feedback form and verbally at events, meetings and informal exchanges.
In a six-week period starting from the beginning of May we received and had 98 exchanges about the project. Of the 98, 95 responses were wholly positive, 2 mixed and 2 negative.
The positive responses echoed one another with the same themes coming up:
- Proud to see their university taking part in No Mow May
- Found the effect beautiful and calming during exam term
- Pleased to see more insects and appreciation of nature on central campus
- Requests to extend the timescale or space
Of the 2 mixed responses, there was some confusion why some areas of campus were still being mown; and that whilst supportive they thought central campus looked scruffy. The 2 negative responses were additionally that it looked scruffy and that it should be elsewhere on campus; and that it was only being done for cost saving measures.
Overall the visual impact was well received by the vast majority. There was a sense that the campus felt fuller and more alive. Respondents were noting down different species that they had seen and a common theme was that they were pleased and proud to see their University taking part.
“Excellent to be part of a University that is looking out for nature. Requires joined up thinking between the sustainability team and estates team. Well done University of Kent.”
Reputationally, the impact of doing something so visual that our staff, students and visitors can see and directly engage with is significant. The cost of this project was extremely low so the impact of the numbers of people that engaged with the project as well as those that just would have walked past and see it is huge and not easily replicated by other engagement activities. People have a desire to see the University being proactive and visible in this space
A lesson learned was that our signage and pre-information could have been better as to inform people which lawns are part of No Mow May. A common question and concern was that people saw mowing happening in other areas (namely courtyards and banks) during May. If we are to do this again we need to look at how we communicate which lawns are included.
We also had people ask why we cut it in June. Why were the lawns not left to grow throughout summer as much evidence shows is better for wildlife?
It was always the intention to cut the No Mow May lawns back in June as the project title suggests. That doesn’t mean the rest of our grasslands were cut at the same time. Only those three lawns in the trial – Registry lawn, front library lawn and side library lawn.
Whilst many of us would like to see the lawns left longer there was some concern about how central campus would look after another month or 2, and how much work it would take to restore the lawns over the winter. Amenity/short cut lawns do serve a purpose on campus for people to sit and gather, as well as for events and recreation. We will never get it perfectly right for everyone in this regard but hopefully our work beyond central campus can demonstrate our commitment to biodiversity beyond May.
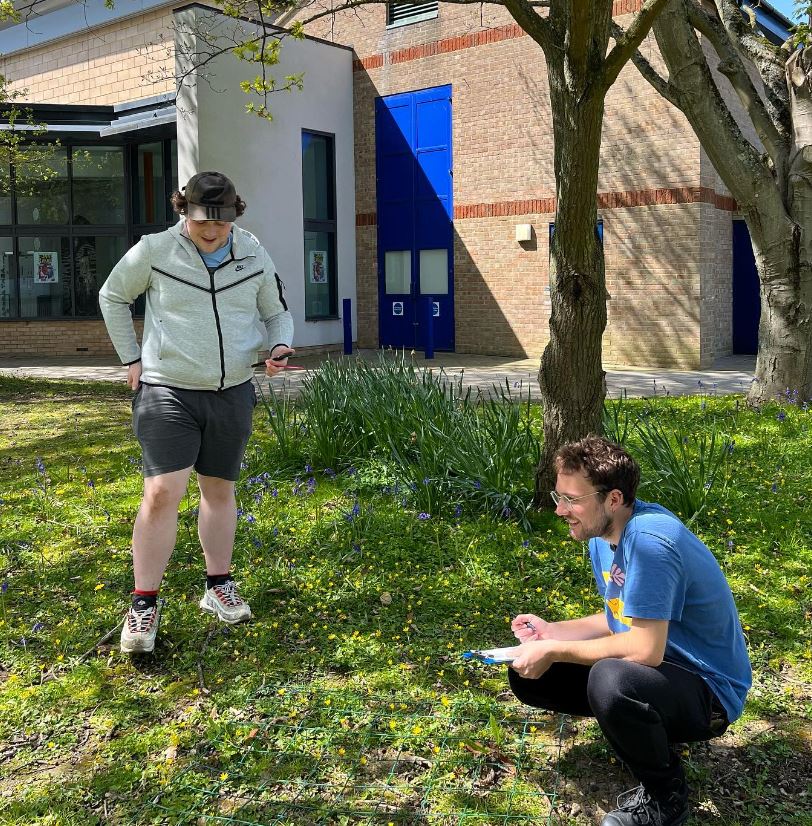

Biodiversity
As part of the trial the Conservation Society carried out a basic vegetation survey at the beginning and end of the month where they measured sward height and species diversity.
Overall, there was an increase in diversity across the lawns surveyed with the exception of Eliot Lawn which was the control lawn and still mown throughout May. This meets our expectation but there were also some interesting surprises that we were not expecting.
Our amenity grassland is much more diverse than it looks, over the course of 4 weeks 41 different species were surveyed without any additional seeding or work, just the absence of mowing. The central campus can be very valuable as a food source if allowed to grow longer. Certain species were flowering within the first two weeks before the sward height started to get really long. Supporting these early flowering species by not mowing in these areas so frequently could support invertebrates beyond Now Mow May.
Further data analysis could be done to look at coverage of certain species. Complimentary surveys of invertebrates should be done during future No Mow May projects.
No Mow May 2024
It is our intention to carry out No Mow May again this year incorporating the feedback we received last year. We hope that this can become an annual project that engages people with our wilder campus brought to the central campus.