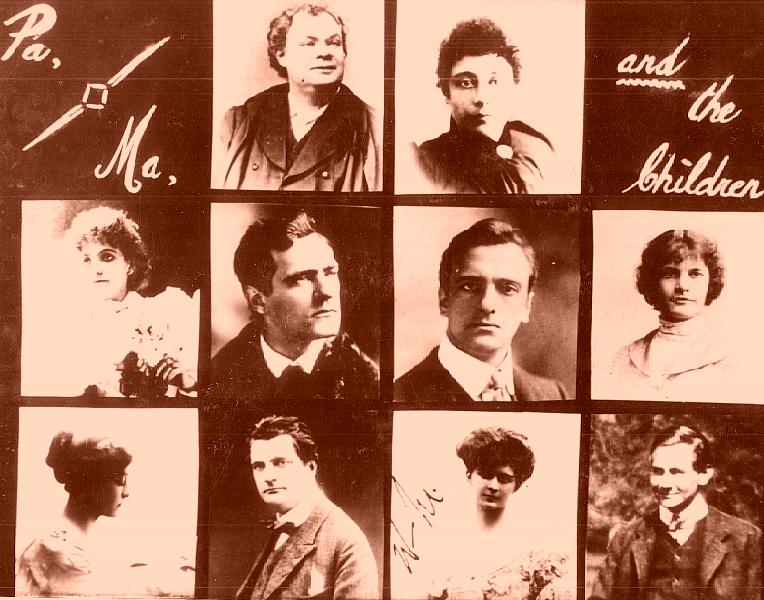
Welcome to part two of our mini series exploring all things musical in Special Collections & Archives – just in time for Kent’s Summer Music Week! Today we’re delving into all things Boucicault and Melville and having a look at some of the amazing art held in the British Cartoon Archive…
Theatre collections part two: Boucicault’s brilliant box-office hits
Ah, Boucicault. The great thing about theatre people is that their history is just as interesting as their works, and the Victorian playwright’s life really is no exception. Bankruptcy? Tick! Extravagant legal battles over copyright of his works? Tick! Affairs and scandal? Tick!

Title page of a Penny Pictorial copy of the play “The Colleen Bawn” by Dion Boucicault, undated (PETT BND 126.33)

Front cover of a Penny Pictorial Play Book of ‘The Colleen Bawn’ by Dion Boucicault, featuring a colour illustration of a scene from the play (BOUC/PHO/0648577)
Drama aside (if that’s possible), Boucicault was arguably one of the most popular writers in the nineteenth century. His plays were immensely popular, in part because they nearly always contained a visual spectacle designed to draw audiences to the box office. In an age before movies and TV, it was a pretty thrilling thing to see – for example – someone nearly drowning in a cave, almost being run over by a train, or a burning house – on stage literally in front of your eyes. But what is possibly less well known about Boucicault is how he was one of the first playwrights to incorporate music specifically written for his works in the theatre; in The Colleen Bawn, not only does the music play alongside dialogue but it actually changes with each line. The music itself was so popular that it was still being loaned out over twenty years after the play was first staged in 1860.

Cover for sheet music accompanying the play “The Colleen Bawn” by Dion Boucicault, c.1861 (CALB/COL/MUS/LDN ADL/F190364)
Boucicault’s use of music in his melodramas also massively helped ease critics into greater support for orchestras on the ‘proper’ theatre stage, showing that drama could extend beyond well-written words into a more complete theatre experience.
The British Cartoon Archive: more than just politics
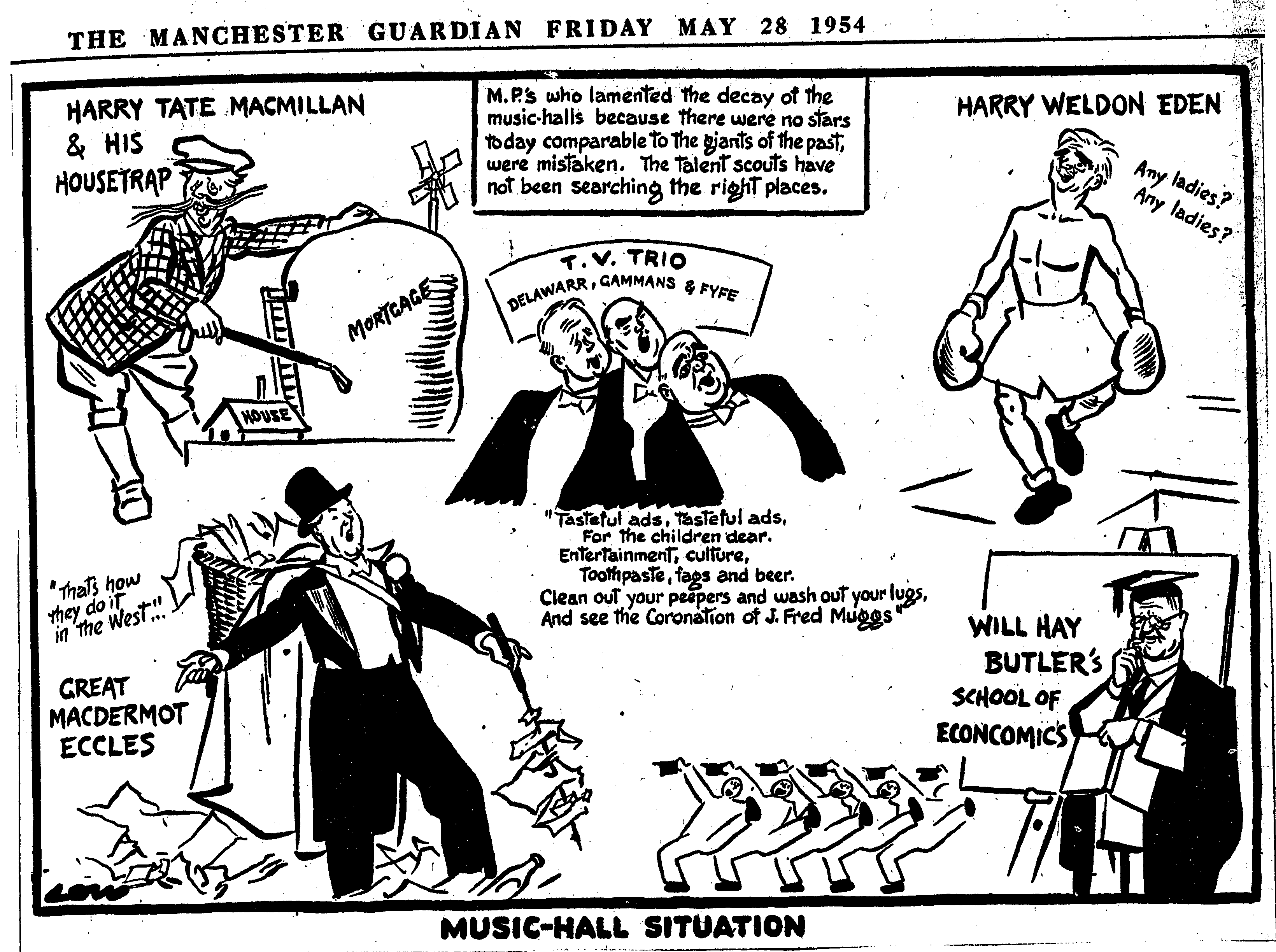
Our British Cartoon Archive is best known for its vast collection of social and political cartoons across the 19th and 20th centuries, so it’s hardly a surprise to discover that music pops up fairly regularly as well. A quick search on our catalogue for ‘music’ returns 146 results! Sometimes music and entertainment is a beautiful hark back to previous times, like in this David Low cartoon from 1954 where the current political situation is reimagined as a music hall variety night:
Occasionally nursery rhymes become mischievously reimagined for contemporary comment, such as in Leslie Illingworth’s retelling of ‘Baa Baa Black Sheep’:
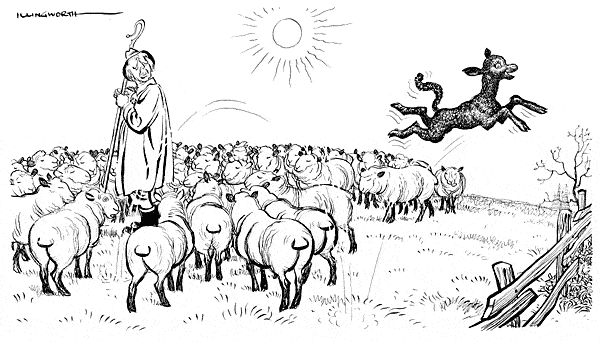
“He’s a poor little lamb who has lost his way, Baa! Baa! Baa!
The little black sheep who has gone astray, Baa! Baa! Baa!
Gentleman Tory off on a spree, D—-d from here to eternity,
Lord have mercy on such as he, Baa! Baa! Baa!
With acknowledgments and apologies to the Whiffenpoof song, published by the Magna Music Co. Ltd.” (Leslie Illingworth, 21 March 1962 for the Daily Mail, ILW3486)
The most regular culprits are – of course – the early 20th century cartoonist W.K. Haselden and the wonderful Carl Giles. For Haselden, whose work in the Daily Mirror tended to look at societal changes as well as political events and wars, the inclusion of music is hardly a leap. Famous for his sketches of actors in Punch and repeated forays into women’s fashion and roles in society, music is another way in which Haselden pokes fun at everyday people and trends:

“Music for the Railway travellers” by W.K. Haselden, published in the Daily Mirror on 04 October 1907 and 20 September 1911 (WH0614)
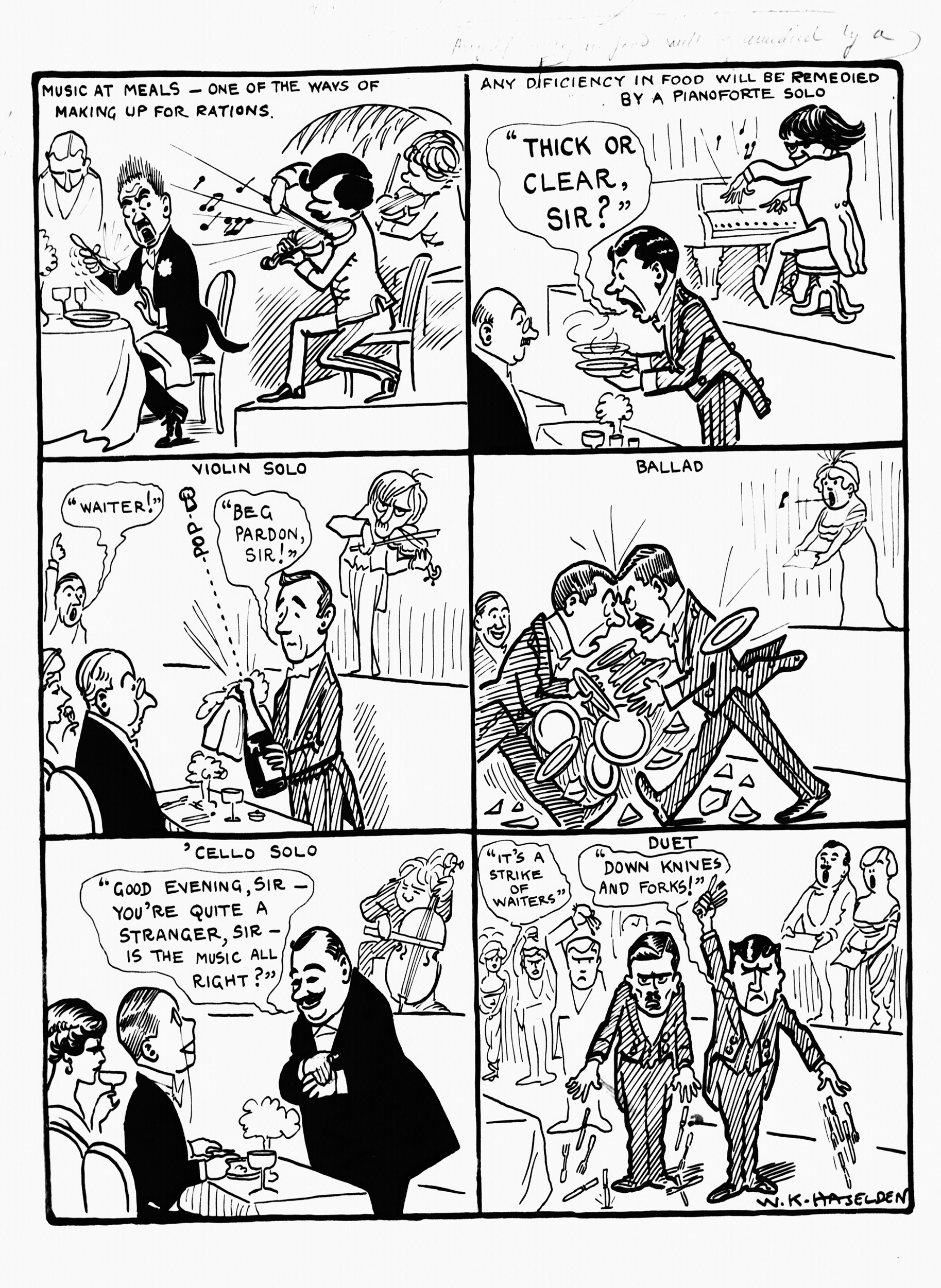

“Music at meals: Meals at music – a parallel” by W.K. Haselden, published in the Daily Mirror on 17 March 1914 and 19 February 1918 (WH0895)
In Carl Giles’ world music is somewhat of a nuisance, especially when it comes to small children attempting to avoid piano lessons:
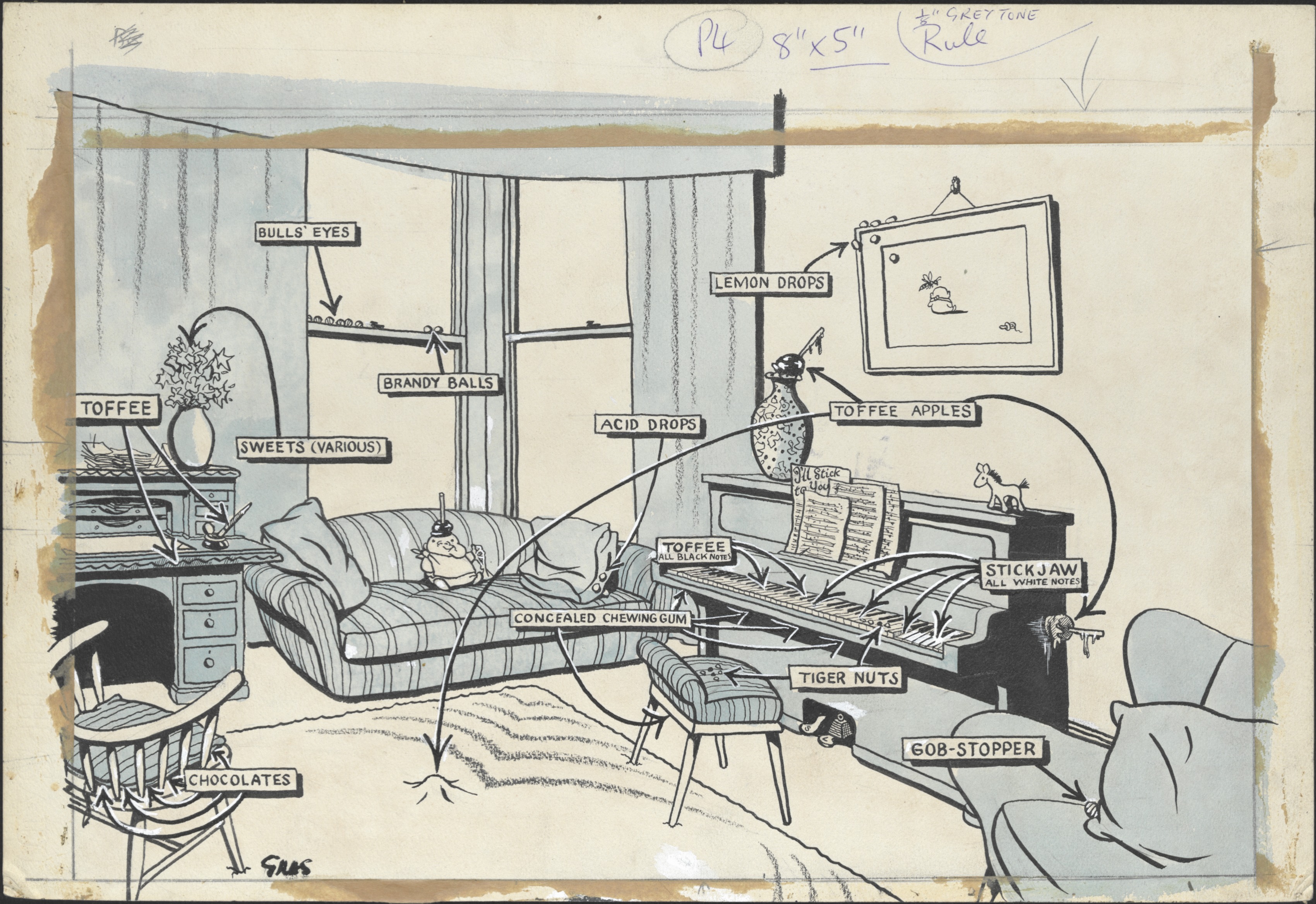
“IN THE GILES FAMILY there is a theory among the children that the more toffee they get on the piano the quicker they get their music lessons over – you press one note and they all go down together. I offer this simple sweets-are-now-off-the-ration guide to parents who, during the more or less sweet-free years, may have forgotten the trouble spots.” (Carl Giles, 7 February 1953 for the Daily Express, GA0825)
Music is also a huge source of mischief in Carl Giles’ land, as seen by this 1959 cartoon:
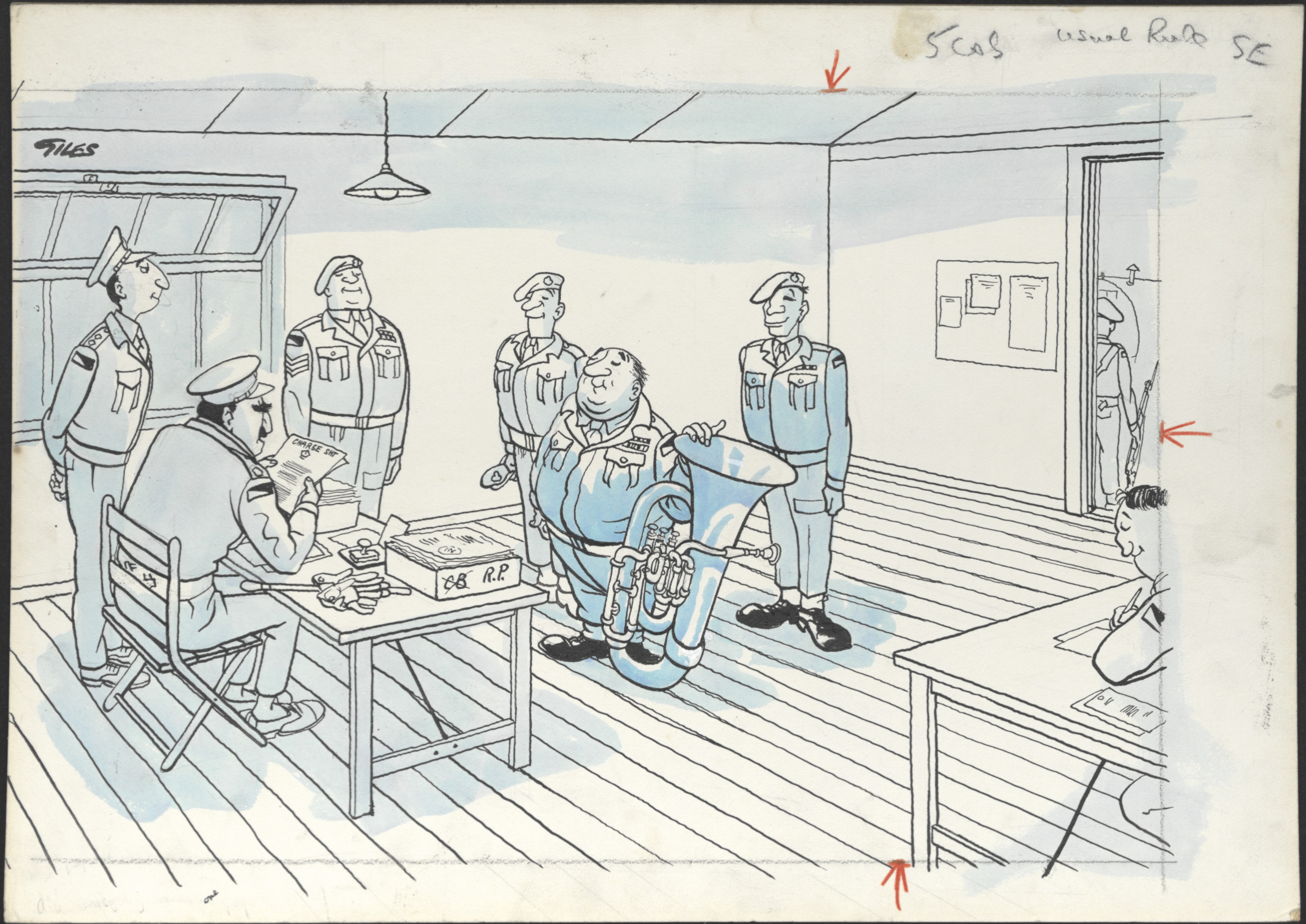
“It is reported that during band practice for the forthcoming visit by Chancellor Adenauer you did wilfully insert one page of ‘Colonel Bogey’ into the band’s music for ‘Deutschland Uber Alles’.” – Carl Giles for the Sunday Express, 15 November 1959 (GA1601)
As you are probably aware, our British Cartoon Archive is such a vast, wide-ranging collection that it’s definitely worth an hour of your time exploring all things musical via the online catalogue. Have fun!
Theatre collections part three: enter the Melvilles stage right
One of the many SC&A hills I am prepared to die on is this: the Melville family, whose complete archives we hold, is criminally underrated in the theatre history world and more people should know about them and love their work. A dynasty of thespians (you can find a brief Twitter-friendly summary of them here), the Melvilles managed several important theatres (including the Theatre Royal Brighton, the Lyceum and the Prince’s / Shaftesbury in London) at the turn of the 19th / early 20th century. But their love of all things drama extended far beyond managing as they wrote and acted in plays as well.
The Melvilles are probably best known for their Bad Woman plays, popular in the early 20th century. The Bad Woman plays are interesting in several ways: they became well known during a time when melodrama as a genre was beginning to wane in theatres, but they also spoke to concerns in early Edwardian society – particularly the role of women during the suffrage movement, when demands for equal rights and pay were becoming ever louder.

Black and white postcard photograph publicising ‘The Bad Girl of the Family’ by Frederick Melville, and showing a scene from the play, c.1909 (MEL/PUBMA/123: 0699937e)
The Melvilles tapped into these concerns and used the melodrama genre to address middle and lower-working class fears about ‘New Women’ disrupting society. As a genre, melodramas always play out social issues on stage before resolving them neatly and the Bad Woman plays did just this, creating unruly female leads who eventually gave up their misbehaving antics to settle down. Music played a huge role in the melodramatic genre; it became integral to the performance, making speech and gestures more extravagant and heightening emotion and meaning throughout.
Alongside the Bad Woman plays the Melvilles worked extensively on a huge range of popular stories, rewriting them for their audiences. We have over 240 play texts from the Melvilles in our archives (view a list of titles here) and many of them contain the original scores for the performances. These plays ranged from pantomimes to contemporary stories, such as First World War dramas (‘The Female Hun’ notably includes sheet music for the German ‘Hymn of Hate’). The amount of music in the Melville archive is also documented through an entire section of the archive catalogue.
We hope you’ve enjoyed this mini-series about music in Special Collections & Archives; do visit our website for more information on the collections and if you have any queries please drop us a line (specialcollections@kent.ac.uk).
Sources:
Boucicault collections:
Fuhrmann, C. Between Opera and Musical: Theatre Music in Early Nineteenth-Century London. In Gordon, R. and Jubin, O. (Eds) The Oxford Handbook of the British Musical. DOI: 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199988747.013.2
Pisani, M. (2004). Music for the theatre: Style and function in incidental music. In K. Powell (Ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Victorian and Edwardian Theatre (Cambridge Companions to Literature, pp. 70-92). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CCOL052179157X.005
Melvilles:
Mayer, D. (2004). Encountering melodrama. In K. Powell (Ed.), The Cambridge Companion to Victorian and Edwardian Theatre (Cambridge Companions to Literature, pp. 145-163). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CCOL052179157X.009